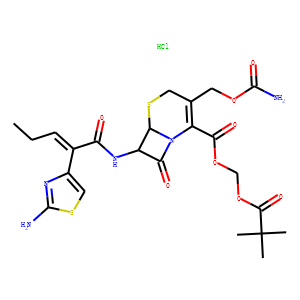
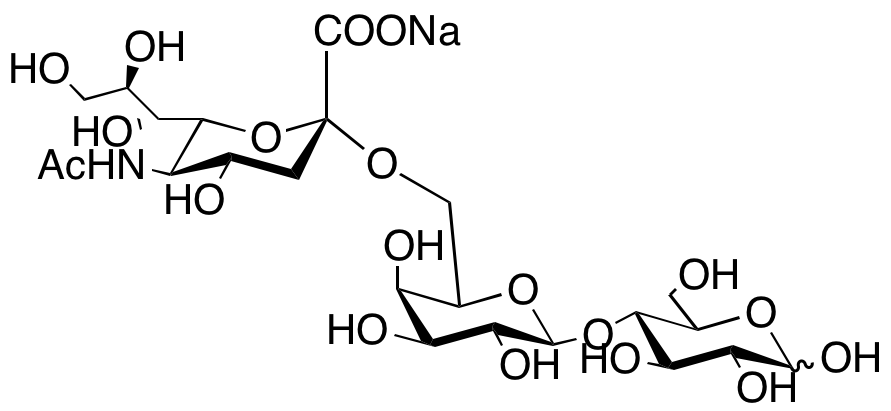
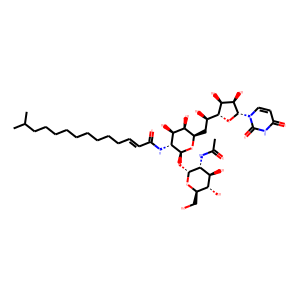
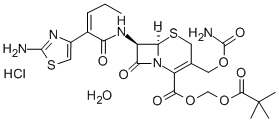
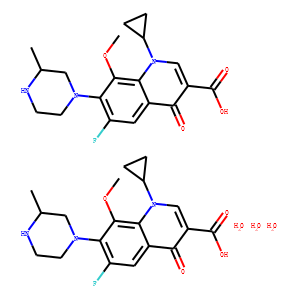
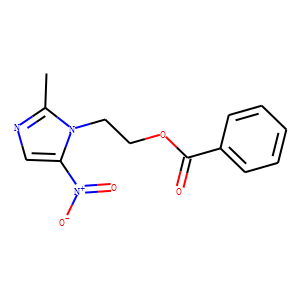
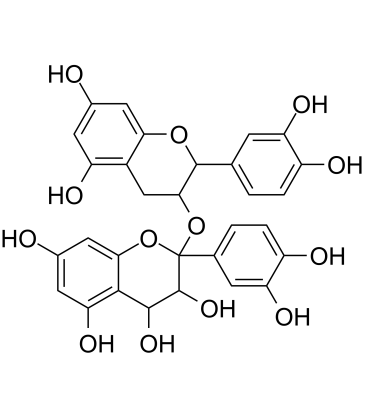
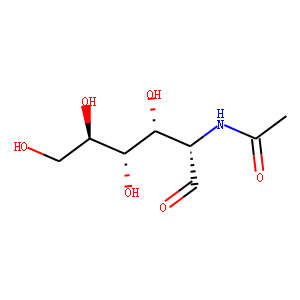
Bacterial
Bacterial targets refer to specific structures or processes in bacteria that are essential for their survival and proliferation, making them ideal for therapeutic intervention. These targets include cell wall synthesis proteins, ribosomes for protein synthesis, DNA replication enzymes, and metabolic pathways unique to bacteria. Antibiotics are designed to exploit these targets, effectively killing bacteria or inhibiting their growth while minimizing harm to human cells. However, the increasing problem of antibiotic resistance, where bacteria evolve to resist these drugs, underscores the need for ongoing research and development of new antimicrobial agents. Novel strategies include bacteriophages, antimicrobial peptides, and inhibitors of resistance mechanisms, aiming to outpace bacterial adaptation and maintain effective bacterial control.