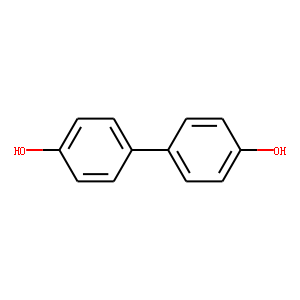
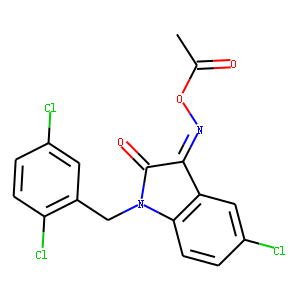
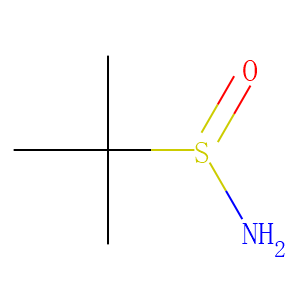
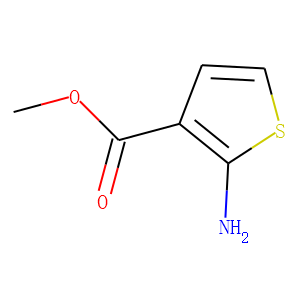
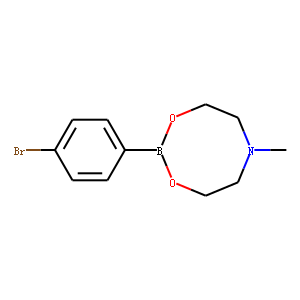
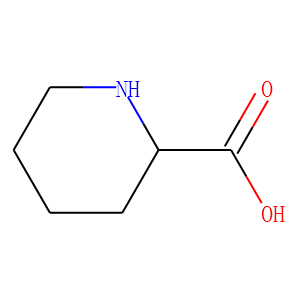
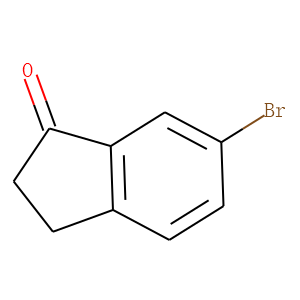
Ubiquitin
Ubiquitination refers to the process in which ubiquitin (a class of low-molecular-weight proteins) molecules, under the action of a series of special enzymes, classify intracellular proteins, select the target protein molecules, and specifically modify the target proteins. These special enzymes include ubiquitin-activating enzymes, binding enzymes, ligating enzymes, and degrading enzymes. Ubiquitination plays an important role in the localization, metabolism, function, regulation, and degradation of proteins. At the same time, it is also involved in the regulation of the cell cycle, proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, metastasis, gene expression, transcriptional regulation, signal transmission, damage repair, inflammation, immunity, and almost all life activities. Ubiquitination is closely related to the pathogenesis of cancer, cardiovascular and other diseases. In recent years, it has become a new target for the research and development of new drugs as an important result of biochemical research.