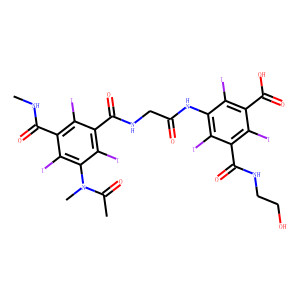
| InChI | InChI=1S/C24H21I6N5O8/c1-7(37)35(3)20-17(29)10(21(39)31-2)13(25)11(18(20)30)23(41)33-6-8(38)34-19-15(27)9(22(40)32-4-5-36)14(26)12(16(19)28)24(42)43/h36H,4-6H2,1-3H3,(H,31,39)(H,32,40)(H,33,41)(H,34,38)(H,42,43) |
| Reference | [1]. Eur J Dermatol. 2001 Mar-Apr;11(2):134-7.<br />
Delayed adverse reaction to sodium ioxaglic acid-meglumine.<br />
Kanny G(1), Marie B, Hoen B, Trechot P, Moneret-Vautrin DA.<br />
Author information: (1)Service de Médecine D, Médecine Interne, Immunologie Clinique et Allergologie, CHU de Nancy, Hôpital Central, 29, avenue de Lattre-de-Tassigny, 54035 Nancy Cedex, France. [email protected]<br />
A patient had a maculopapular rash, fever, hepatic cytolysis, rhabdomyolysis, eosinophilia and raised total IgEs after coronarography with ioxaglic acid-meglumine (Hexabrix). Intradermal test to ioxaglic acid-meglumine was positive 48 hrs later. Histological examination revealed perivascular lymphocytic infiltration, with predominantly CD45Ro+ and CD8+ T cells and apoptotic basal keratinocytes. This case documents a late hypersensitivity reaction to ioxaglic acid-meglumine.<br />
PMID: 11275812 [Indexed for MEDLINE]<br />
<br />
[2]. Invest Radiol. 1984 Nov-Dec;19(6 Suppl):S289-392.<br />
Ioxaglic acid: a new low-osmolality contrast medium.<br />
[No authors listed]<br />
PMID: 6511272 [Indexed for MEDLINE]<br />
<br />
[3]. Pathol Biol (Paris). 1987 Nov;35(9):1215-20.<br />
[Comparative pharmacokinetics and renal accumulation of the iodized contrast media: ioxitalamic acid, ioxaglic acid and iohexol in the rabbit].<br />
[Article in French]<br />
Morin JP(1), Boutelet I, Toutain H, Fillastre JP.<br />
Author information: (1)INSERM U-295, UER de Médecine et de Pharmacie, Saint-Etienne-du-Rouvrais, France.<br />
Male and female rabbits were given a I.V. bolus injection of a single 5 ml/kg dose of either ioxitalamic acid, ioxaglic acid or iohexol. Animals were killed 2 hours, 8 hours and 24 hours after the injection. One group of animals received a continuous I.V. infusion of contrast agent at a constant rate of 2.5 ml/kg/hour of four hours. Animals were killed 30 minutes after the end of the infusion. Plasma and tissue concentrations of contrast agents were assayed using an HPLC method. A pharmacokinetic study was performed after the I.V. bolus injection. This study shows that: 1) Plasma elimination half-lives were identical in males and in females as well as for all three products. This half life is about 45 minutes. The distribution volume was identical in male and females as well as for all three products and was comprised between 20% and 26% of body weight. 2) For all three contrast agents, the renal cortical concentrations are higher than in the medulla or the papilla at all the observation times. The renal cortical accumulation of contrast agents is persistent in comparison to plasma concentrations. 3) Ionic and lipophilic properties of contrast agents seem to play an important role on the renal accumulation pattern.<br />
PMID: 3320896 [Indexed for MEDLINE]<br />
<br />
[4]. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh). 1983;24(1):43-7. doi: 10.1177/028418518302400109.<br />
Effects of ioxaglic acid on cardiac functions during coronary arteriography in canines.<br />
Trägårdh B, Lynch PR.<br />
The new monoacid dimer ioxaglic acid (P286), The non-ionic metrizamide (Amipaque) and diatrizoate (Renografin 76) were compared regarding their effects on left ventricular pressure, the first derivative of left ventricular pressure, aortic pressures and on ECG changes during left and right coronary angiography in dogs. Ioxaglate was found to affect most of these parameters less than diatrizoate probably due to its lower osmolality. Ioxaglate should be regarded suitable for coronary angiography. However, ioxaglate was found to have greater effects on the cardiac function than the equiosmolar metrizamide. This is probably due to the chemotoxicity of the anion or possibly to the sodium content of the ioxaglic acid solution.<br />
DOI: 10.1177/028418518302400109 PMID: 6869056 [Indexed for MEDLINE]<br />
<br />
[5]. Allergy. 1998 Dec;53(12):1133-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1998.tb03832.x.<br />
Detection of IgE antibody to a radiocontrast medium.<br />
Mita H(1), Tadokoro K, Akiyama K.<br />
Author information: (1)Clinical Research Center, National Sagamihara Hospital, Kanagawa, Japan.<br />
Comment in Allergy. 1998 Dec;53(12):1111-3.<br />
BACKGROUND: Very little is known about the mechanisms underlying adverse reactions to radiocontrast medium. On the basis of the clinical features of the adverse reactions, it has generally been considered that an IgE-dependent mechanism is not involved in these adverse reactions, and only a few studies have demonstrated the presence of IgE antibody to radiocontrast medium in patient sera. METHODS: We assayed for IgE antibody to ioxaglic acid (Hexabrix), a representative radiocontrast medium, in the sera of patients who had developed adverse reactions to ioxaglic acid. A conjugate was prepared by coupling succinyl ioxaglic acid to human serum albumin. Enzyme immunoassay and radioimmunoassay for the detection of IgE antibody to ioxaglic acid in patient sera were constructed by physical adsorption or by covalent coupling of the conjugate on solid supports. RESULTS: When the radioactivity or the absorbance exceeding the mean plus 3 SD for normal healthy subjects was regarded as positive, IgE antibody was detected in the sera of 47.1% of the patients who had a past history of adverse reactions to ioxaglic acid and 16.2% of those who had experienced adverse reactions to ioxaglic acid within 24 h before the blood collection, although the IgE antibody levels were low. On the other hand, IgE antibody to ioxaglic acid was not detected in the sera of patients with no history of adverse reactions to ioxaglic acid. Inhibition experiments revealed the presence of IgE antibody specific to ioxaglic acid in the serum defined as positive for IgE antibody to ioxaglic acid. The presence of IgE antibody to ioxaglic acid did not always correlate with the activation of mast cells due to the occurrence of adverse reactions to ioxaglic acid. CONCLUSIONS: A small amount of IgE antibody to ioxaglic acid was detected in the sera of some patients with a history of adverse reactions to ioxaglic acid, and these adverse reactions may be partly explained by the presence of IgE antibody in the serum of at least some patients.<br />
DOI: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1998.tb03832.x PMID: 9930588 [Indexed for MEDLINE]
|