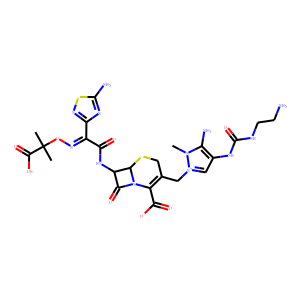
| InChI | InChI=1S/C23H30N12O8S2/c1-23(2,20(40)41)43-31-11(15-30-21(26)45-32-15)16(36)29-12-17(37)35-13(19(38)39)9(8-44-18(12)35)6-34-7-10(14(25)33(34)3)28-22(42)27-5-4-24/h7,12,18,25H,4-6,8,24H2,1-3H3,(H7,26,27,28,29,30,32,36,38,39,40,41,42)/b31-11-/t12-,18-/m1/s1 |
| Reference | [1]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Dec;57(12):5924-30. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00656-13. Epub 2013 Sep 16.<br />
Pharmacological basis of β-lactamase inhibitor therapeutics: tazobactam in combination with Ceftolozane.<br />
Vanscoy B(1), Mendes RE, McCauley J, Bhavnani SM, Bulik CC, Okusanya OO, Forrest A, Jones RN, Friedrich LV, Steenbergen JN, Ambrose PG.<br />
Author information:<br />
(1)Institute for Clinical Pharmacodynamics, Latham, New York, USA.<br />
We recently investigated the pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics (PK-PD) of tazobactam in combination with ceftolozane against an isogenic CTX-M-15-producing Escherichia coli triplet set, genetically engineered to transcribe different levels of blaCTX-M-15. The percentage of the dosing interval that tazobactam concentrations remained above a threshold (%Time>threshold) was identified as the PK-PD exposure measure that was most closely associated with efficacy. Moreover, the tazobactam concentration was dependent upon the enzyme transcription level. Given that the aforementioned strains were genetically engineered to transcribe a single β-lactamase enzyme and that clinical isolates typically produce multiple β-lactamase enzymes with various transcription levels, it is likely that the tazobactam threshold concentration is isolate/enzyme dependent. Our first objective was to characterize the relationship between the tazobactam %Time>threshold in combination with ceftolozane and efficacy using clinical isolates in an in vitro PK-PD infection model. Our second objective was to identify a translational relationship that would allow for the comodeling across clinical isolates. The initial challenge panel included four well-characterized β-lactamase-producing E. coli strains with variable enzyme expression and other resistance determinants. As evidenced by r(2) values of ranging from 0.90 to 0.99 for each clinical isolate, the observed data were well described by fitted functions describing the relationship between the tazobactam %Time>threshold and change in log10 CFU from baseline; however, the data from the four isolates did not comodel well. The threshold concentration identified for each isolate ranged from 0.5 to 4 mg/liter. We identified an enabling translational relationship for the tazobactam threshold that allowed comodeling of all four clinical isolates, which was the product of the individual isolate's ceftolozane-tazobactam MIC value and 0.5. As evidenced by an r(2) value of 0.90, the transformed data were well described by a fitted function describing the relationship between tazobactam %Time>threshold and change in log10 CFU from baseline. Due to these findings, the challenge panel was expanded to include three well-characterized β-lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae strains with variable enzyme expression and other resistance determinants. The translational relationship for the tazobactam threshold that allowed for the comodeling of the four E. coli isolates performed well for the expanded data set (seven isolates in total; four E. coli and three K. pneumoniae), as evidenced by an r(2) value of 0.84. This simple translational relationship is especially useful as it is directly linked to in vitro susceptibility test results, which are used to guide the clinician's choice of drug and dosing regimen.<br />
<br />
<br />
[2]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Nov;57(11):5707-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01404-13. Epub 2013 Aug 12.<br />
In vitro activity of ceftolozane-tazobactam against Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates obtained from patients in Canadian hospitals in the CANWARD study, 2007 to 2012.<br />
Walkty A(1), Karlowsky JA, Adam H, Baxter M, Lagacé-Wiens P, Hoban DJ, Zhanel GG.<br />
Author information:<br />
(1)Departments of Medicine and Clinical Microbiology, Health Sciences Centre.<br />
The in vitro activity of ceftolozane in combination with tazobactam (fixed concentration of 4 μg/ml) was evaluated against 2,435 Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates obtained from across Canada using Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute broth microdilution methods. The MIC50 and MIC90 values for ceftolozane-tazobactam were 0.5 μg/ml and 1 μg/ml, respectively (a 32-fold-lower MIC90 than that for ceftazidime). Eighty-nine percent (141/158) of multidrug-resistant isolates were inhibited by ≤8 μg/ml of ceftolozane-tazobactam.<br />
<br />
<br />
[3]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Apr;57(4):1577-82. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01590-12. Epub 2012 Dec 28.<br />
In vivo activities of ceftolozane, a new cephalosporin, with and without tazobactam against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacteriaceae, including strains with extended-spectrum β-lactamases, in the thighs of neutropenic mice.<br />
Craig WA(1), Andes DR.<br />
Author information:<br />
(1)Department of Medicine, University of Wisconsin and William S Middleton VA Hospital, Madison, Wisconsin, USA. [email protected]<br />
Ceftolozane is a new cephalosporin with potent activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacteriaceae. A neutropenic murine thigh infection model was used to determine which pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic index and magnitude drives the efficacy of ceftolozane with Gram-negative bacilli, to compare the rates of in vivo killing of P. aeruginosa by ceftolozane and ceftazidime, and to determine the impact of different ratios of ceftolozane plus tazobactam on Enterobacteriaceae containing extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs). Neutropenic mice had 10(6.2-7.1) CFU/thigh when treated with ceftolozane for 24 h with (i) various doses (3.12 to 1,600 mg/kg) and dosage intervals (3, 6, 12, and 24 h) against two Enterobacteriaceae strains, (ii) 0.39 to 800 mg/kg every 6 h for four Enterobacteriaceae and four P. aeruginosa strains, and (iii) 400 or 800 mg/kg with 2:1. 4:1, and 8:1 ratios of tazobactam against five Enterobacteriaceae strains with ESBLs. The pharmacokinetics of ceftolozane at 25, 100, and 400 mg/kg were linear with peak/dose values of 1.0 to 1.4 and half-lives of 12 to 14 min. T>MIC was the primary index driving efficacy. For stasis (1 log kill), T>MIC was 26.3% ± 2.1% (31.6% ± 1.6%) for wild-type Enterobacteriaceae, 31.1% ± 4.9% (34.8% ± 4.4%) for Enterobacteriaceae with ESBLs, and 24.0% ± 3.3% (31.5% ± 3.9%) for P. aeruginosa. At 200 mg/kg every 3 h, the rate of in vivo killing of P. aeruginosa was faster with ceftolozane than with ceftazidime (-0.34 to -0.41 log10 CFU/thigh/h versus -0.21 to -0.24 log10 CFU/thigh/h). The 2:1 ratio of ceftolozane with tazobactam was the most potent combination studied. The T>MIC required for ceftolozane is less than with other cephalosporins and may be due to more rapid killing.<br />
<br />
<br />
[4]. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013 Jan;68(1):177-83. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks343. Epub 2012 Aug 30.<br />
Efficacy of ceftolozane in a murine model of Pseudomonas aeruginosa acute pneumonia: in vivo antimicrobial activity and impact on host inflammatory response.<br />
Jacqueline C(1), Roquilly A, Desessard C, Boutoille D, Broquet A, Le Mabecque V, Amador G, Potel G, Caillon J, Asehnoune K.<br />
Author information:<br />
(1)Université de Nantes, Faculté de Médecine, Thérapeutiques Cliniques et Expérimentales des Infections, EA 3826, F-44000 Nantes, France. [email protected]<br />
OBJECTIVES: To assess the activity of ceftolozane, a novel oxyimino-cephalosporin, in comparison with ceftazidime and piperacillin/tazobactam against a multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain using a murine model of pneumonia.<br />
METHODS: Quantitative bacteriology, survival, histological examination, myeloperoxidase activity, proinflammatory cytokine levels in lungs and endothelial permeability were evaluated to determine the effects of ceftolozane and comparators on P. aeruginosa-induced pneumonia.<br />
RESULTS: After 48 h of treatment, ceftolozane reduced the bacterial load by 3-4 log(10) cfu/g of lung. Systemic dissemination of the pulmonary infection and development of lung damage were inhibited in all β-lactam-treated animals. P. aeruginosa-induced pneumonia led to elevated concentrations of tumour necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β and macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-2 in the lungs. While the levels of proinflammatory cytokines decreased following ceftazidime and piperacillin/tazobactam therapy, ceftolozane exhibited increased concentrations of IL-1β and MIP-2 after 24 h of infection, resulted in significantly increased levels of recruited neutrophils within the infected lung without increasing lung endothelial permeability.<br />
CONCLUSIONS: These data strongly support ceftolozane as an effective option for the treatment of severe P. aeruginosa respiratory infections by improving the early pulmonary inflammatory response without impairing 48 h post-infection homeostasis.<br />
|