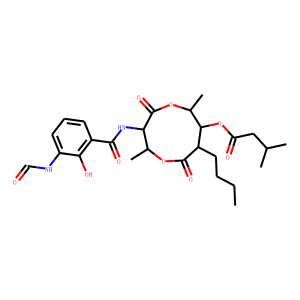
| Reference | <span style=”color:#000000;”><span style=”font-family:arial,helvetica,sans-serif;”><span style=”font-size:12px;”>1.Yonehara H. & Takeuchi S. J. Studies on the chemical structure of blastmycin. Antibiotics Ser. A 11, 254 (1958).</span></span></span><br />
<span style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0);”>2.</span><span class=”authors” data-text=”Barrow, C.J., Oleynek, J.J., Marinelli, V., et al.” style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box; font-variant-ligatures: normal; orphans: 2; widows: 2;”><span style=”box-sizing: border-box;”><span class=”scientificMarkup” style=”box-sizing: border-box;”>Barrow, C.J., Oleynek, J.J., Marinelli, V., <span class=”foreign” style=”box-sizing: border-box; font-style: italic;”>et al</span>.</span></span></span><span class=”title” data-text=”Antimycins, inhibitors of ATP-citrate lyase, from a Streptomyces sp.” style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box; font-variant-ligatures: normal; orphans: 2; widows: 2;”> <span style=”box-sizing: border-box;”><span class=”scientificMarkup” style=”box-sizing: border-box;”>Antimycins, inhibitors of ATP-<wbr style=”box-sizing: border-box;” />citrate lyase, from a <span class=”species” style=”box-sizing: border-box; font-style: italic;”>Streptomyces</span> sp.</span></span></span><span class=”journal” style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box; font-style: italic; font-variant-ligatures: normal; orphans: 2; widows: 2;”> J. Antibiot. (Tokyo)</span><span class=”number” style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box; font-weight: 700; font-variant-ligatures: normal; orphans: 2; widows: 2;”> </span><span class=”pagerange” style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box; font-variant-ligatures: normal; orphans: 2; widows: 2;”>50(9), 729-733</span><span class=”year” style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box; font-variant-ligatures: normal; orphans: 2; widows: 2;”> (1997)</span><span style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-variant-ligatures: normal; orphans: 2; widows: 2;”>.</span><br />
<span style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-variant-ligatures: normal; orphans: 2; widows: 2;”>3.</span><span class=”authors” data-text=”Takimoto, H., Machida, K., Ueki, M., et al.” style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box; font-variant-ligatures: normal; orphans: 2; widows: 2;”><span style=”box-sizing: border-box;”><span class=”scientificMarkup” style=”box-sizing: border-box;”>Takimoto, H., Machida, K., Ueki, M., <span class=”foreign” style=”box-sizing: border-box; font-style: italic;”>et al</span>.</span></span></span><span class=”title” data-text=”UK-2A, B, C and D, novel antifungal antibiotics from Streptomyces sp. 517-02 IV. Comparative studies of UK-2A with antimycin A3 on cytotoxic activity and reactive oxygen species generation in LLC-PK1 cells” style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box; font-variant-ligatures: normal; orphans: 2; widows: 2;”> <span style=”box-sizing: border-box;”><span class=”scientificMarkup” style=”box-sizing: border-box;”>UK-<wbr style=”box-sizing: border-box;” />2A, B, C and D, novel antifungal antibiotics from <span class=”species” style=”box-sizing: border-box; font-style: italic;”>Streptomyces</span> sp. 517-<wbr style=”box-sizing: border-box;” />02 IV. Comparative studies of UK-<wbr style=”box-sizing: border-box;” />2A with antimycin A<sub style=”box-sizing: border-box; position: relative; font-size: 12px; line-height: 0; bottom: -0.25em;”>3</sub> on cytotoxic activity and reactive oxygen species generation in LLC-<wbr style=”box-sizing: border-box;” />PK1 cells</span></span>.</span><span class=”journal” style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box; font-style: italic; font-variant-ligatures: normal; orphans: 2; widows: 2;”> J. Antibiot. (Tokyo)</span><span class=”number” style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box; font-weight: 700; font-variant-ligatures: normal; orphans: 2; widows: 2;”> </span><span class=”pagerange” style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box; font-variant-ligatures: normal; orphans: 2; widows: 2;”>52(5),480-484</span><span class=”year” style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); box-sizing: border-box; font-variant-ligatures: normal; orphans: 2; widows: 2;”> (1999)</span><span style=”font-family: arial, helvetica, sans-serif; color: rgb(0, 0, 0); font-variant-ligatures: normal; orphans: 2; widows: 2;”>.</span>
|