| Reference | [1]. J Fluoresc. 2016 Nov;26(6):2199-2212. doi: 10.1007/s10895-016-1916-y. Epub 2016 Sep 13.<br />
Graphene Quantum Dots Functionalized with 4-Amino-2, 2, 6, 6-Tetramethylpiperidine-N-Oxide as Fluorescence "Turn-ON" Nanosensors.<br />
Achadu OJ(1), Britton J(1), Nyokong T(2).<br />
Author information: (1)Department of Chemistry, Rhodes University, Grahamstown, South Africa. (2)Department of Chemistry, Rhodes University, Grahamstown, South Africa. [email protected].<br />
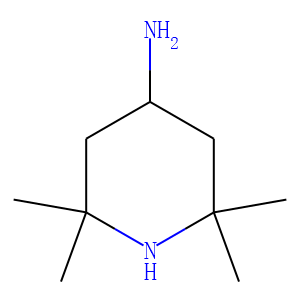
In this study, we report on the fabrication of simple and rapid graphene quantum dots (GQDs)-based fluorescence "turn-ON" nanoprobes for sensitive and selective detection of ascorbic acid (AA). Pristine GQDs and S and N co-doped-GQDs (SN-GQDs) were functionalized with 4-amino-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-N-oxide (4-amino-TEMPO, a nitroxide free radical). The nitroxide free radicals efficiently quenched the fluorescence of the GQDs and upon interaction of the nanoconjugates with ascorbic acid, the quenched fluorescence was restored. The linear ranges recorded were 0.5-5.7 μM and 0.1-5.5 μM for GQDs-4-amino-TEMPO and SN-GQDs-4amino-TEMPO nanoprobes, respectively. Limits of detection were found to be 60 nM and 84 nM for SN-GQDS-4-amino-TEMPO and GQDs-4-amino-TEMPO for AA detection, respectively. This novel fluorescence "turn-ON" technique showed to be highly rapid and selective towards AA detection.<br />
DOI: 10.1007/s10895-016-1916-y PMID: 27624186<br />
<br />
[2]. Nat Protoc. 2013 Apr;8(4):666-76. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.028. Epub 2013 Mar 7.<br />
Synthesis of 4-acetamido-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxoammonium tetrafluoroborate and 4-acetamido-(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-piperidin-1-yl)oxyl and their use in oxidative reactions.<br />
Mercadante MA(1), Kelly CB, Bobbitt JM, Tilley LJ, Leadbeater NE.<br />
Author information: (1)Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, Connecticut, USA.<br />
We describe the synthesis of the lesser-known stoichiometric oxidation reagent 4-acetamido-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxoammonium tetrafluoroborate (1, Bobbitt's salt), as well as of 4-acetamido-(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-piperidin-1-yl)oxyl (2, AcNH-TEMPO). Several representative oxidation reactions are also presented to demonstrate the salt's oxidative capabilities. Bobbitt's salt has a range of applications, from the oxidation of various alcohols to their corresponding carbonyl derivatives to the oxidative cleavage of benzyl ethers, whereas 2 has been shown to serve as a catalytic or stoichiometric oxidant. The oxyl radical can be obtained in 85% yield over two steps on a 1-mole scale from commercially available 4-amino-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine (5), and is far more cost-effective to prepare in-house than purchase commercially. An additional step converts the oxyl radical into the oxoammonium salt (1, Bobbitt's salt) in 88% yield, with an overall yield of 75%. The synthesis of the salt takes ∼5 d to complete. Oxoammonium salts are metal-free, nontoxic and environmentally friendly oxidants. Preparation of 1 is also inherently 'green', as water can be used as the solvent and the use of environmentally unfriendly materials is minimal. Moreover, after it has been used, the spent oxidant can be recovered and used to regenerate 1, thereby making the process recyclable.<br />
DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2013.028 PMID: 23471111 [Indexed for MEDLINE]<br />
<br />
[3]. Biosens Bioelectron. 2011 Jul 15;26(11):4632-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2011.05.020. Epub 2011 May 19.<br />
A nanoprobe for nonprotein thiols based on assembling of QDs and 4-amino-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine oxide.<br />
Xu K(1), Chen H, Wang H, Tian J, Li J, Li Q, Li N, Tang B.<br />
Author information: (1)Engineering Research Center of Pesticide and Medicine Intermediate Clean Production, Ministry of Education, Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Clean Production of Fine Chemicals, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, PR China.<br />
A new fluorescent nanoprobe, 4-amino-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine oxide (AT)-functionalized CdTe quantum dots (QDs-AT), was synthesized, for selective detection of nonprotein thiols based on electron transfer (ET). In the presence of nonprotein thiols, the nitroxide radicals in QDs-AT were converted to hydroxylamines, resulting in the fluorescence recovery of the quenched QDs. The detection mechanism of the probe was investigated using Rh-Se-2 probe. The nanoprobe has high sensitivity toward glutathione (GSH) with a detection limit of 7.1 × 10⁻⁸ M. The fluorescent imaging of living cells showed that QDs-AT could distinguish the concentration differences of GSH in HL-7702 and HepG2 cells.<br />
DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2011.05.020 PMID: 21646008 [Indexed for MEDLINE]<br />
<br />
[4]. J Phys Chem B. 2006 Aug 24;110(33):16353-8. doi: 10.1021/jp061115d.<br />
Free radical sensor based on CdSe quantum dots with added 4-amino-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine oxide functionality.<br />
Maurel V(1), Laferrière M, Billone P, Godin R, Scaiano JC.<br />
Author information: (1)Department of Chemistry, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Ontario K1N 6N5, Canada.<br />
The association and resulting fluorescence quenching of CdSe quantum dots by 4-amino-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine oxide (4-amino-TEMPO), a persistent nitroxide, have been examined using electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) and fluorescence spectroscopy. EPR data suggest binding constants around (8 +/- 4) x 10(6) M(-1) for green (2.4-2.5 nm) nanoparticles, and the application of Job's method indicates that the preferred mode of binding involves one or two quencher molecules per quantum dot, although more quenchers could bind at high concentrations of 4-amino-TEMPO. Fluorescence quenching by 4-amino-TEMPO is at least 3 orders of magnitude more efficient than by TEMPO itself, reflecting the strong binding confirmed by the EPR data. Stern-Volmer plots are nonlinear and in light of the EPR data probably reflect ready accessibility of the CdSe surface to one or two 4-amino-TEMPO molecules, while additional quenchers can only bind if they displace trioctylphosphine oxide ligands. Quantum dot-4-amino-TEMPO complexes can be used as free radical sensors, since the fluorescence (quenched by the nitroxide) is readily restored when radicals are trapped to form alkoxyamines.<br />
DOI: 10.1021/jp061115d PMID: 16913763 [Indexed for MEDLINE]<br />
<br />
[5]. Langmuir. 2011 Oct 18;27(20):12709-19. doi: 10.1021/la2029565. Epub 2011 Sep 13.<br />
Assemblies of functional small-sized molecules having 4-amino-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl responsive to heat and pH in water and their water proton relaxivities.<br />
Hayashi H(1), Ohkubo K, Karasawa S, Koga N.<br />
Author information: (1)Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Kyushu University, 3-1-1 Maidashi, Fukuoka 812-8582, Japan.<br />
1,3,5-Triureabenzene derivatives carrying alkyl (C(n)) and poly(ethylene glycol) (Eg(m)) chains C(n)Eg(3) (1, 2, and 3, n = 6, 7, and 8, respectively) and C(n)N(X)Eg(m) (4 and 5, X = M (methyl), n = 6 and 8, respectively, m = 3; 6 and 7, X = T (2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl, TEMPO), n = 6, m = 3 and 6, respectively) were prepared. All compounds in aqueous solutions exhibited the lower critical solution temperature (LCST) phenomena unique for small-sized molecules and formed self-assemblies above the transition temperature, T(t), of the LCST. Only compound 3 formed a hydrogel with a minimum gelation concentration of 0.5 mM (0.05 wt %). In 1.0 mM aqueous solution, the T(t) values were determined to be in the range of 12-40 °C. In addition, the T(t) values for 4-7 containing tertiary amine also responded to the solution pH with high sensitivity. The LCST behaviors for all compounds were reversible in the cycles of warming and cooling. The water proton relaxivities, r(1), for 6 and 7 carrying TEMPO were altered below and above T(t) and were largely reduced by the formation of self-assemblies above T(t). Compound 6 showed r(1) values at 25 °C of 0.92 and 0.23 mM(-1) s(-1) at pH 7.0 and 6.0, respectively. In transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images, globular particles with polydispersity were observed, and their average hydrodynamic diameters (D(H)) were determined to be in the range of 2400-730 nm by dynamic light scattering. In the TEM and scanning electron microscopy images of a xerogel sample of 3, bundles of fibers with a diameter of ca. 10 nm and a network structure, respectively, were observed.<br />
DOI: 10.1021/la2029565 PMID: 21875113 [Indexed for MEDLINE]
|