Why is Sodium Hyaluronate So Popular in Recent Years?
Sodium hyaluronate, also known as the hyaluronic acid sodium salt, is a naturally occurring polysaccharide that holds significant importance in various fields, including medicine, cosmetics, and food supplements. Derived from hyaluronic acid, it exhibits unique properties, making it a valuable substance for numerous applications.
With a molecular weight in the range of millions, sodium hyaluronate is characterized by its ability to retain water molecules. This property contributes to its role in maintaining hydration and lubrication in the body, particularly in connective tissues, joints, and skin.
In the medical realm, sodium hyaluronate finds extensive use as a viscoelastic agent in ophthalmic surgeries, aiding in maintaining intraocular space and protecting delicate eye structures. Furthermore, it is employed in orthopedics to improve joint mobility and alleviate pain, particularly in conditions like osteoarthritis. Dermatology utilizes sodium hyaluronate in topical creams, injections, and dermal fillers, harnessing its moisturizing and anti-aging effects to enhance skin health and appearance.
In the cosmetic industry, sodium hyaluronate is prized for its hydrating capabilities. It can attract and retain moisture, plumping the skin and reducing the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. Its inclusion in various skincare products, such as moisturizers, serums, and masks, contributes to its effectiveness in maintaining skin moisture and suppleness.
Moreover, sodium hyaluronate is available as a dietary supplement, offering potential benefits for joint health and skin hydration when taken orally.
Overall, sodium hyaluronate’s diverse applications and properties make it a valuable ingredient in several industries, contributing to enhanced well-being, appearance, and quality of life.
Chemical Structure and Properties
Sodium hyaluronate has a unique chemical structure composed of repeating disaccharide units. These units consist of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, connected by glycosidic bonds. The presence of negatively charged carboxylate and sulfate groups contributes to its water-attracting properties.
Due to its high molecular weight, sodium hyaluronate forms a viscous gel when hydrated, making it an excellent water-binding substance. This property enables it to retain moisture, providing hydration and lubrication in various applications.
The chemical structure and properties of sodium hyaluronate play a crucial role in its biological functions, medical applications, and cosmetic benefits. Understanding its molecular arrangement helps explain its ability to maintain tissue hydration, its viscoelastic behavior, and its effectiveness as a moisturizer and anti-aging agent in skincare products.
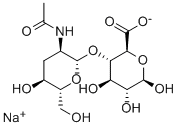
Fig1 The structural formula of Sodium hyaluronate
Natural Occurrence and Biological Role
Sodium hyaluronate is naturally present in various tissues of the human body, including connective tissues, joints, and skin. It serves a crucial biological role as a hydrating and lubricating agent. Attracting and retaining water molecules helps maintain tissue hydration and flexibility. Sodium hyaluronate is a vital component of the extracellular matrix, providing structural support to cells and aiding in tissue repair and regeneration. It also acts as a shock absorber in joints and helps keep the skin hydrated, supple, and resilient.
Medical Applications of Sodium Hyaluronate
Sodium hyaluronate, due to its unique properties, finds extensive use in various medical fields. Let’s explore its applications in ophthalmology, orthopedics, and dermatology.
Ophthalmology
In ophthalmology, sodium hyaluronate serves as a viscoelastic agent during surgical procedures. During cataract extraction or intraocular lens implantation, it is used to maintain the anterior chamber’s depth, protecting delicate ocular structures and facilitating surgical maneuvers. Sodium hyaluronate acts as a temporary space filler and creates a protective cushion, preventing damage to the cornea, iris, and lens. Additionally, it aids in minimizing postoperative inflammation and promoting faster healing.
Orthopedics
Sodium hyaluronate has proven beneficial in orthopedic applications, particularly in the treatment of osteoarthritis. In this condition, the synovial fluid that lubricates the joints becomes thinner and less effective. By injecting sodium hyaluronate into the joint space, it acts as a supplement to the diminished synovial fluid, providing improved lubrication and shock absorption. This can reduce pain, increase joint mobility, and improve overall function. Sodium hyaluronate injections are commonly performed in the knee, but they can also be used in other joints such as the hip or shoulder.
Dermatology
In dermatology, sodium hyaluronate offers several applications for skincare and cosmetic purposes. It is a key ingredient in topical creams, serums, and masks due to its exceptional hydrating properties. Sodium hyaluronate can attract and retain water molecules, providing intense moisture to the skin. This helps improve skin hydration, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and enhance skin elasticity and firmness. Additionally, it acts as a humectant, creating a protective barrier on the skin’s surface to prevent moisture loss. Sodium hyaluronate is also utilized in dermal fillers, where it is injected into specific areas of the face to restore volume, smooth wrinkles, and enhance facial contours.
In summary, sodium hyaluronate plays a valuable role in ophthalmology, orthopedics, and dermatology. Its use as a viscoelastic agent in ophthalmic surgeries, joint lubrication in osteoarthritis, and skin hydration in dermatology highlight its versatility and potential benefits across different medical specialties.
Cosmetic and Skincare Uses
Sodium hyaluronate is a highly sought-after ingredient in the cosmetic and skincare industry due to its exceptional moisturizing and anti-aging properties. Let’s delve into its various uses and benefits in this field.
Hydration and Moisturization: Sodium hyaluronate has a remarkable ability to attract and retain water molecules. When applied topically, it helps to hydrate the skin by replenishing moisture levels. It forms a film on the skin’s surface, preventing water loss and maintaining a healthy moisture barrier. This hydration effect can lead to smoother, plumper, and more supple skin.
Anti-aging Effects: As we age, the natural production of hyaluronic acid in the skin diminishes, resulting in the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines. Incorporating sodium hyaluronate into skin care products can help address these signs of aging. It can penetrate the skin’s layers and promote hydration, improving the appearance of wrinkles and giving the skin a more youthful and rejuvenated look.
Dermal Fillers: Sodium hyaluronate is also used in the form of injectable dermal fillers. These filters, composed of cross-linked hyaluronic acid, are used to restore volume and minimize the appearance of deep wrinkles and facial folds. They can enhance facial contours, plump up areas such as the lips or cheeks, and provide a more youthful appearance. The effects of these fillers are temporary, with results typically lasting several months to a year.
Compatibility and Safety: Sodium hyaluronate is generally well-tolerated by most individuals, as it is a naturally occurring substance in the body. It has a low risk of allergic reactions and is considered compatible with different skin types. However, as with any cosmetic or skincare product, it’s important to follow the instructions and consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist if needed.
In conclusion, sodium hyaluronate is widely utilized in cosmetics and skincare products for its exceptional moisturizing and anti-aging properties. Its ability to hydrate the skin, reduce the appearance of wrinkles, and provide volumizing effects through dermal fillers has made it a popular ingredient in the pursuit of youthful and radiant skin.
Research and Development
The research and development (R&D) of sodium hyaluronate continue to drive innovation and expand its applications. Scientists and researchers are actively exploring new formulations, delivery methods, and potential therapeutic uses of this versatile compound. Ongoing studies focus on optimizing its properties, enhancing stability, and improving its efficacy in various medical, cosmetic, and skincare applications. R&D efforts also aim to discover novel derivatives or combinations of sodium hyaluronate with other substances to enhance its benefits. This research plays a crucial role in advancing our understanding of sodium hyaluronate and expanding its potential applications to address evolving needs in healthcare, cosmetics, and beyond.
Comparison to Other Hyaluronic Acid Derivatives
Sodium hyaluronate is just one of several hyaluronic acid derivatives used in various applications. When comparing sodium hyaluronate to other derivatives, factors such as molecular weight, viscosity, and cross-linking play a significant role. For example, higher molecular weight derivatives tend to have greater viscoelastic properties and are commonly used in ophthalmic and orthopedic applications. Cross-linked derivatives, such as those found in dermal fillers, offer longer-lasting results due to their reduced degradation rate. Different derivatives may also vary in terms of their tissue affinity and rheological properties, making them more suitable for specific applications. Comparative studies often evaluate aspects like bioavailability, biocompatibility, and clinical outcomes to determine the most appropriate derivative for a particular use. Ultimately, the selection of a hyaluronic acid derivative depends on the desired application and the specific properties required for optimal effectiveness and patient satisfaction.
Future Prospects and Potential Applications
Sodium hyaluronate continues to hold great promise for future developments and expanded applications in various fields. Here are some potential areas where it may find new uses:
Regenerative Medicine: Researchers are exploring the potential of sodium hyaluronate in regenerative medicine. It has shown promise in tissue engineering applications, where it can serve as a scaffold for cell growth and tissue regeneration. Combining sodium hyaluronate with stem cells or growth factors may enhance its regenerative capabilities, opening doors for repairing damaged tissues and organs.
Wound Healing: Sodium hyaluronate’s ability to promote tissue regeneration and maintain a moist wound environment makes it an intriguing candidate for advanced wound healing applications. Researchers are investigating its use in chronic wound management, such as diabetic ulcers or burns, to enhance healing rates and improve outcomes.
Drug Delivery Systems: The unique properties of sodium hyaluronate make it an ideal candidate for drug delivery systems. It can be formulated into hydrogels, nanoparticles, or microparticles to encapsulate and deliver drugs with controlled release profiles. This offers targeted and sustained drug delivery opportunities, particularly in dermatology, ophthalmology, and orthopedics.
Cosmetic Enhancements: The cosmetic industry is continuously exploring new ways to improve anti-aging and aesthetic procedures. Sodium hyaluronate may be further developed to enhance dermal fillers, optimizing their longevity and natural-looking results. Additionally, innovative skincare formulations could harness its moisturizing properties to address specific skin concerns and improve overall skin health.
Artificial Intelligence and Personalized Medicine: Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning with sodium hyaluronate research may lead to personalized treatment approaches. AI algorithms could help determine optimal dosages, formulations, and treatment plans based on individual patient characteristics, allowing for more tailored and effective interventions.
It’s important to note that these potential applications are still under investigation, and further research is needed to fully explore their feasibility and safety. Nevertheless, the prospects for sodium hyaluronate suggest exciting advancements in medicine, wound care, drug delivery, cosmetics, and personalized healthcare.
References:
- Abatangelo G, Vindigni V, Avruscio G, Pandis L, Brun P. Hyaluronic Acid: Redefining Its Role. Cells. 2020 Jul 21;9(7):1743. doi 10.3390/cells9071743. PMID: 32708202; PMCID: PMC7409253.
- Juncan AM, Moisă DG, Santini A, Morgovan C, Rus LL, Vonica-Țincu AL, Loghin F. Advantages of Hyaluronic Acid and Its Combination with Other Bioactive Ingredients in Cosmeceuticals. Molecules. 2021 Jul 22;26(15):4429. doi 10.3390/molecules26154429. PMID: 34361586; PMCID: PMC8347214.
- Bronstone A, Neary JT, Lambert TH, Dasa V. Supartz (Sodium Hyaluronate) for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review of Efficacy and Safety. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2019 Apr 12;12:1179544119835221. doi 10.1177/1179544119835221. PMID: 31019370; PMCID: PMC6463231.
- Kobayashi T, Chanmee T, Itano N. Hyaluronan: Metabolism and Function. Biomolecules. 2020 Nov 7;10(11):1525. doi 10.3390/biom10111525. PMID: 33171800; PMCID: PMC7695009.
- Bayer IS. Hyaluronic Acid and Controlled Release: A Review. Molecules. 2020 Jun 6;25(11):2649. doi 10.3390/molecules25112649. PMID: 32517278; PMCID: PMC7321085.
- Gupta RC, Lall R, Srivastava A, Sinha A. Hyaluronic Acid: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Trajectory. Front Vet Sci. 2019 Jun 25;6:192. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00192. PMID: 31294035; PMCID: PMC6603175.