Vortioxetine, a Novel Antidepressant with Multimodal Activity
Abstract
Vortioxetine is a novel antidepressant that has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its unique pharmacological profile and potential therapeutic benefits.[1] It belongs to a class of drugs known as multimodal antidepressants, which means it exerts its effects through multiple mechanisms of action within the brain.
Introduction
A. Introduction to Vortioxetine
Vortioxetine is a novel antidepressant that has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its unique pharmacological profile and potential therapeutic benefits.[1] It belongs to a class of drugs known as multimodal antidepressants, which means it exerts its effects through multiple mechanisms of action within the brain.
Vortioxetine’s primary mechanism of action involves the inhibition of serotonin reuptake, similar to traditional selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). However, what sets vortioxetine apart is its additional modulation of serotonin receptors, particularly the 5-HT1A receptor. By acting as a partial agonist at this receptor, vortioxetine not only increases serotonin levels but also fine-tunes the serotonin signaling system, potentially enhancing its antidepressant effects.
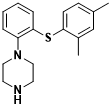
Figure 1 Chemical Structure of Vortioxetine
B. Rationale for Multimodal Antidepressants
The development of multimodal antidepressants like vortioxetine arises from the need for more effective and well-tolerated treatments for depression and related mood disorders. Conventional antidepressants, while effective for many individuals, often come with limitations, such as delayed onset of action and undesirable side effects.[2]
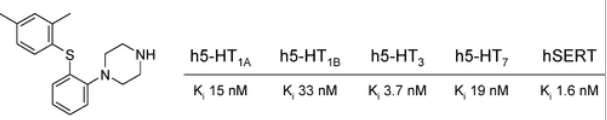
Figure 2 Vortioxetine displays high affinity for recombinant human 5-HT1A (Ki = 15 nM), 5-HT1B (Ki = 33 nM), 5-HT3A (Ki = 3.7 nM), 5-HT7 (Ki = 19 nM), and noradrenergic β1 (Ki = 46 nM) receptors, and SERT (Ki = 1.6 nM).[2]
Multimodal antidepressants aim to address these limitations by targeting multiple aspects of the neurobiological underpinnings of depression. By simultaneously modulating serotonin reuptake and receptor activity, vortioxetine seeks to provide a more comprehensive and faster-acting solution for individuals suffering from depressive disorders.
Furthermore, the rationale for multimodal antidepressants extends to improving cognitive function, which is often impaired in individuals with depression. Vortioxetine’s unique pharmacological properties are associated with cognitive enhancement, making it a promising option not only for alleviating depressive symptoms but also for addressing cognitive deficits often observed in depressed patients.
Preclinical Data
A. Mechanism of Action
Serotonin Reuptake Inhibition
Vortioxetine’s mechanism of action primarily involves the inhibition of serotonin reuptake, a mechanism shared with conventional selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). It functions by blocking the reuptake of serotonin, a neurotransmitter crucial for mood regulation, into presynaptic neurons. By inhibiting this reuptake, vortioxetine increases the concentration of serotonin in the synaptic cleft, leading to enhanced serotonin signaling in the brain. This heightened serotonin activity is thought to contribute to the antidepressant effects of vortioxetine by improving mood and emotional stability.[3]
What distinguishes vortioxetine from classical SSRIs is its additional modulation of serotonin receptors, particularly the 5-HT1A receptor. While SSRIs primarily impact serotonin reuptake, vortioxetine acts as a partial agonist at the 5-HT1A receptor. This unique property allows vortioxetine to not only elevate serotonin levels but also fine-tune the serotonin system. By acting as a partial agonist, it can stimulate this receptor when serotonin levels are low and dampen its activity when they are high, thereby optimizing serotonin signaling in a way that is conducive to mood regulation.
5-HT Receptor Modulation
In addition to its interaction with the 5-HT1A receptor, vortioxetine also affects other serotonin receptors. It acts as an antagonist at the 5-HT3 receptor, which is believed to play a role in mood and anxiety regulation. By antagonizing this receptor, vortioxetine may further enhance its antidepressant effects by modulating serotonin-mediated responses in the brain.
B. Neurobiological Effects
Effects on Serotonin Signaling
Vortioxetine’s impact on serotonin signaling goes beyond simple reuptake inhibition. Its multifaceted actions on serotonin receptors result in a more nuanced and balanced modulation of serotoninergic pathways. This unique approach is particularly relevant in the context of mood disorders like depression, where dysregulated serotonin signaling is a hallmark.
By acting as a partial agonist at the 5-HT1A receptor, vortioxetine not only increases serotonin levels but also fine-tunes the responsiveness of this receptor to serotonin. This modulation is thought to improve the therapeutic profile of vortioxetine by maintaining optimal serotonin receptor activity. Moreover, its antagonism at the 5-HT3 receptor further refines the serotonergic balance, potentially reducing excessive serotonin activity associated with side effects seen in some traditional SSRIs.
Impact on Neuroplasticity
Neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize itself, is a fundamental process in mood regulation and cognitive function. Vortioxetine’s actions on serotonin receptors and neurotransmitter systems have implications for neuroplasticity. Some preclinical studies suggest that vortioxetine may enhance neuroplasticity by promoting the growth and branching of neurons, particularly in brain regions associated with mood regulation and cognitive processing.[4]
This effect on neuroplasticity could underlie vortioxetine’s unique cognitive-enhancing properties, which are not typically seen with conventional antidepressants. By promoting neuroplastic changes in the brain, vortioxetine may not only alleviate depressive symptoms but also address cognitive deficits often observed in individuals with mood disorders.
In summary, vortioxetine’s preclinical data highlights its intricate mechanism of action, encompassing serotonin reuptake inhibition and modulation of multiple serotonin receptors. These actions result in a balanced and nuanced impact on serotonin signaling and neuroplasticity, setting vortioxetine apart as a promising candidate for the treatment of depression and related mood disorders. Further exploration of these preclinical findings provides valuable insights into the potential therapeutic benefits of vortioxetine in the clinical setting.
Clinical Data
A. Efficacy in Depressive Disorders
Antidepressant Effects
Clinical studies have demonstrated that vortioxetine exhibits robust antidepressant effects in individuals suffering from depressive disorders. In randomized controlled trials, vortioxetine has consistently shown superiority over placebo in reducing the severity of depressive symptoms. Its multimodal mechanism of action, which includes serotonin reuptake inhibition and receptor modulation, contributes to its effectiveness.
Notably, vortioxetine’s unique pharmacological profile sets it apart from traditional antidepressants. By targeting multiple facets of the serotonin system, it may provide a more comprehensive approach to mood regulation. This is particularly relevant for individuals who do not respond adequately to standard antidepressant treatments, offering them a potential alternative for symptom relief.
Improvement in Cognitive Function
Beyond its antidepressant effects, vortioxetine has garnered attention for its ability to enhance cognitive function. Many individuals with depressive disorders experience cognitive deficits, including difficulties with memory, attention, and decision-making. Vortioxetine’s impact on cognitive function may represent a significant therapeutic advantage.
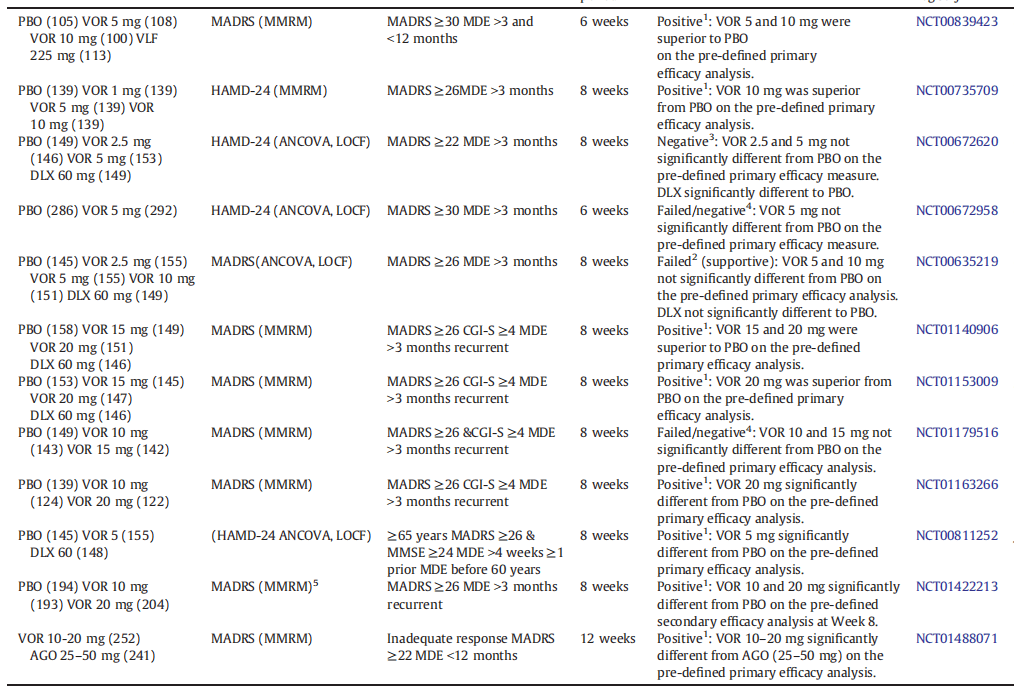
Table 1 Overview of short-term (6–8 weeks) randomized, double-blind placebo controlled clinical studies in MDD patients. FAS: full analysis set, PBO: placebo, VOR: vortioxetine, VLF: venlafaxine, DLX: duloxetine, AGO: agomelatine MDE: major depressive episode.[5]
Clinical studies have reported improvements in cognitive performance in patients treated with vortioxetine. This cognitive enhancement is believed to be linked to its effects on neuroplasticity and the modulation of neurotransmitter systems beyond serotonin. It suggests that vortioxetine has the potential not only to alleviate depressive symptoms but also to address the cognitive impairments often associated with depression.
B. Safety and Tolerability
Adverse Effects Profile
In assessing the safety and tolerability of vortioxetine, it is essential to consider its adverse effects profile. While vortioxetine is generally well-tolerated, it is not without side effects. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and gastrointestinal disturbances. However, these side effects are often transient and tend to diminish over time.
Compared to some traditional antidepressants, vortioxetine may have a more favorable side effect profile, with fewer reports of sexual dysfunction and weight gain. This makes it a potentially attractive option for individuals concerned about these common side effects associated with certain antidepressants.[6]
Comparison to Other Antidepressants
One of the strengths of vortioxetine lies in its unique pharmacological properties and its potential to address the limitations of existing antidepressants. When compared to traditional SSRIs, vortioxetine’s multimodal action may offer advantages in terms of both efficacy and tolerability. Additionally, its cognitive-enhancing effects set it apart from many other antidepressants, making it a compelling option for individuals struggling with cognitive deficits alongside their depressive symptoms.
Target Receptors and Pathways
A. Serotonin Receptors
Vortioxetine’s pharmacological actions extend beyond simple serotonin reuptake inhibition. Central to its mechanism of action is its interaction with various serotonin receptors. Notably, it acts as a partial agonist at the 5-HT1A receptor, which plays a pivotal role in mood regulation. By modulating this receptor, vortioxetine fine-tunes serotonin signaling, potentially enhancing its antidepressant effects.
Additionally, vortioxetine functions as an antagonist at the 5-HT3 receptor. This interaction further refines its impact on serotoninergic pathways, reducing the risk of excessive serotonin activity and associated side effects. Understanding these interactions with serotonin receptors provides insights into how vortioxetine achieves its multimodal antidepressant effects.
B. Other Relevant Neurotransmitter Systems
While serotonin plays a central role, vortioxetine’s effects extend to other neurotransmitter systems as well. It influences norepinephrine and dopamine systems to a certain extent, although the extent and clinical significance of these actions are not as well-established as its serotonin-related effects.[7]
These interactions with various neurotransmitter systems contribute to the complexity of vortioxetine’s mechanism of action and its potential to address both mood symptoms and cognitive deficits. Further research is ongoing to elucidate the full extent of its interactions with these systems and their relevance in the treatment of depressive disorders and related conditions.
Use in Specific Fields
A. Pharmaceutical Applications
Treatment of Depression
One of the primary pharmaceutical applications of vortioxetine lies in the treatment of depression. Clinical studies have consistently demonstrated its efficacy in reducing the severity of depressive symptoms. Its multimodal mechanism of action, which combines serotonin reuptake inhibition with receptor modulation, provides a comprehensive approach to mood regulation.
Vortioxetine’s unique ability to fine-tune serotonin signaling, particularly through partial agonism of the 5-HT1A receptor, sets it apart from traditional antidepressants. This nuanced modulation may explain its effectiveness, even in cases where other antidepressants have proven less successful. As a result, vortioxetine has become a valuable option for individuals who do not respond adequately to standard treatments.
Potential in Other Mood Disorders
Beyond depression, vortioxetine shows promise in the treatment of other mood disorders. Preliminary studies suggest its potential in conditions such as generalized anxiety disorder and bipolar depression. While further research is needed to establish its efficacy in these areas, vortioxetine’s unique pharmacological profile makes it a compelling candidate for broader applications within the realm of mood disorders.
B. Organic Chemistry
Synthesis and Structural Considerations
Vortioxetine’s organic chemistry aspects are of interest to researchers and pharmaceutical chemists. Its complex chemical structure poses intriguing challenges in synthesis and structural analysis. The synthesis of vortioxetine involves multiple steps, including the creation of key intermediates and the assembly of its intricate molecular framework. Understanding these synthetic pathways is essential for ensuring efficient and cost-effective production.
Moreover, the structural considerations of vortioxetine have implications for its pharmacological properties. The presence of various functional groups and chiral centers in its structure influences its interactions with biological targets, such as serotonin receptors. Organic chemists play a critical role in elucidating the structure-activity relationships that underlie vortioxetine’s therapeutic effects.
C. Material Chemistry
Potential Applications in Materials Science
While primarily recognized for its pharmaceutical applications, vortioxetine’s properties may have unexplored potential in the field of materials science. The synthesis of vortioxetine involves the manipulation of molecular structures, which could inspire innovative approaches in materials design.
Exploring the interaction of vortioxetine with materials at the nanoscale or studying its potential as a precursor for novel organic materials could open up new avenues in material chemistry. While this area remains speculative and requires further investigation, it underscores the diverse range of applications that can emerge from the study of complex organic compounds like vortioxetine.
Summary
Vortioxetine, a novel antidepressant with a multimodal mechanism of action, has garnered significant attention in the field of psychiatry. This compound, introduced as a promising treatment option for depressive disorders, functions by inhibiting serotonin reuptake, akin to traditional SSRIs, but it goes further by modulating serotonin receptors, most notably the 5-HT1A receptor, offering a unique fine-tuning of serotonin signaling. Preclinical studies reveal vortioxetine’s potential to promote neuroplasticity, enhancing the growth and branching of neurons, which may explain its cognitive-enhancing effects. Clinical data supports its efficacy in alleviating depressive symptoms and, notably, improving cognitive function, addressing a critical aspect of depression often overlooked by conventional treatments. Furthermore, vortioxetine’s safety profile is favorable, with fewer reports of sexual dysfunction and weight gain compared to some other antidepressants. Its interactions with serotonin receptors and other neurotransmitter systems contribute to its complex mechanism of action, setting it apart as a multimodal antidepressant. Beyond psychiatry, vortioxetine’s organic chemistry aspects pose intriguing challenges and opportunities in synthesis and structural analysis, while its potential applications in material chemistry remain speculative. In conclusion, vortioxetine emerges as a multifaceted antidepressant with a unique pharmacological profile, offering promise in the treatment of mood disorders, particularly depression, and potential insights into various scientific domains.
Reference
- Artigas, F. (1993). 5-HT and antidepressants: New views from microdialysis studies.
Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 14(7), 262. - Bang-Andersen, B., Ruhland, T., Jørgensen, M., Smith, G., Frederiksen, K., Jensen, K. G., & Stensbøl, T. B. (2011). Discovery of 1-[2-(2, 4-dimethylphenylsulfanyl) phenyl] piperazine (Lu AA21004): A novel multimodal compound for the treatment of major depressive disorder.
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 54(9), 3206-3221. - Hjorth, S. (1993). Serotonin 5-HT1A autoreceptor blockade potentiates the ability of the 5-HT reuptake inhibitor citalopram to increase nerve terminal output of 5-HT in vivo: A microdialysis study.
Journal of Neurochemistry, 60(2), 776-779. - Haddjeri, N., Etievant, A., Pehrson, A., Sanchez, C., & Betry, C. (2012). Effects of the multimodal antidepressant Lu AA21004 on rat synaptic and cellular hippocampal plasticity and memory recognition.
European Neuropsychopharmacology, 22(Suppl. 2), S303. - Sanchez, C., Asin, K. E., & Artigas, F. (2015). Vortioxetine, a novel antidepressant with multimodal activity: Review of preclinical and clinical data.
Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 145, 43-57. - Theunissen, E. L., Street, D., Højer, A. M., Vermeeren, A., Van Oers, A., & Ramaekers, J. G. (2013). A randomized trial on the acute and steady-state effects of a new antidepressant, vortioxetine (Lu AA21004), on actual driving and cognition.
Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 93(6), 493-501. - Li, Y., Pehrson, A. L., Budac, D. P., Sánchez, C., & Gulinello, M. (2012). A rodent model of premenstrual dysphoria: Progesterone withdrawal induces depression-like behavior that is differentially sensitive to classes of antidepressants.
Behavioural Brain Research, 234(2), 238-247.