Telisotuzumab Vedotin-tllv (EMRELIS™): A Precision Therapy Breakthrough for c-MET–Positive Lung Cancer
Abstract
Telisotuzumab vedotin-tllv (EMRELIS™) is an FDA-approved antibody-drug conjugate for adults with c-MET–positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have progressed after prior systemic therapy. By combining a monoclonal antibody targeting the c-MET receptor with a cytotoxic payload (MMAE), EMRELIS™ delivers targeted cell killing with reduced systemic toxicity. Clinical trials have shown high objective response rates, especially in patients with high c-MET expression. With a manageable safety profile and ongoing research into expanded indications and combinations, EMRELIS™ marks a significant advancement in biomarker-driven oncology. Its approval highlights the growing impact of precision medicine and the evolving role of ADCs in solid tumor treatment strategies.
Introduction: What is Telisotuzumab Vedotin-tllv?
Telisotuzumab vedotin-tllv, marketed under the brand name EMRELIS™, represents a major advancement in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), particularly in patients whose tumors express the c-MET receptor. Recently granted accelerated approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in May 2025, EMRELIS™ offers a new therapeutic option for adults with c-MET–positive NSCLC who have previously undergone systemic treatment.
The c-MET receptor is a proto-oncogene often overexpressed in various cancers, including NSCLC, and is associated with aggressive tumor behavior and poor prognosis. Prior to this approval, treatment options for c-MET–positive NSCLC were limited, especially for patients who had already received standard therapies such as platinum-based chemotherapy or immune checkpoint inhibitors.
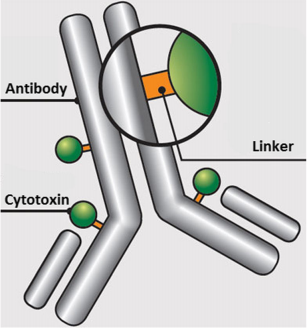
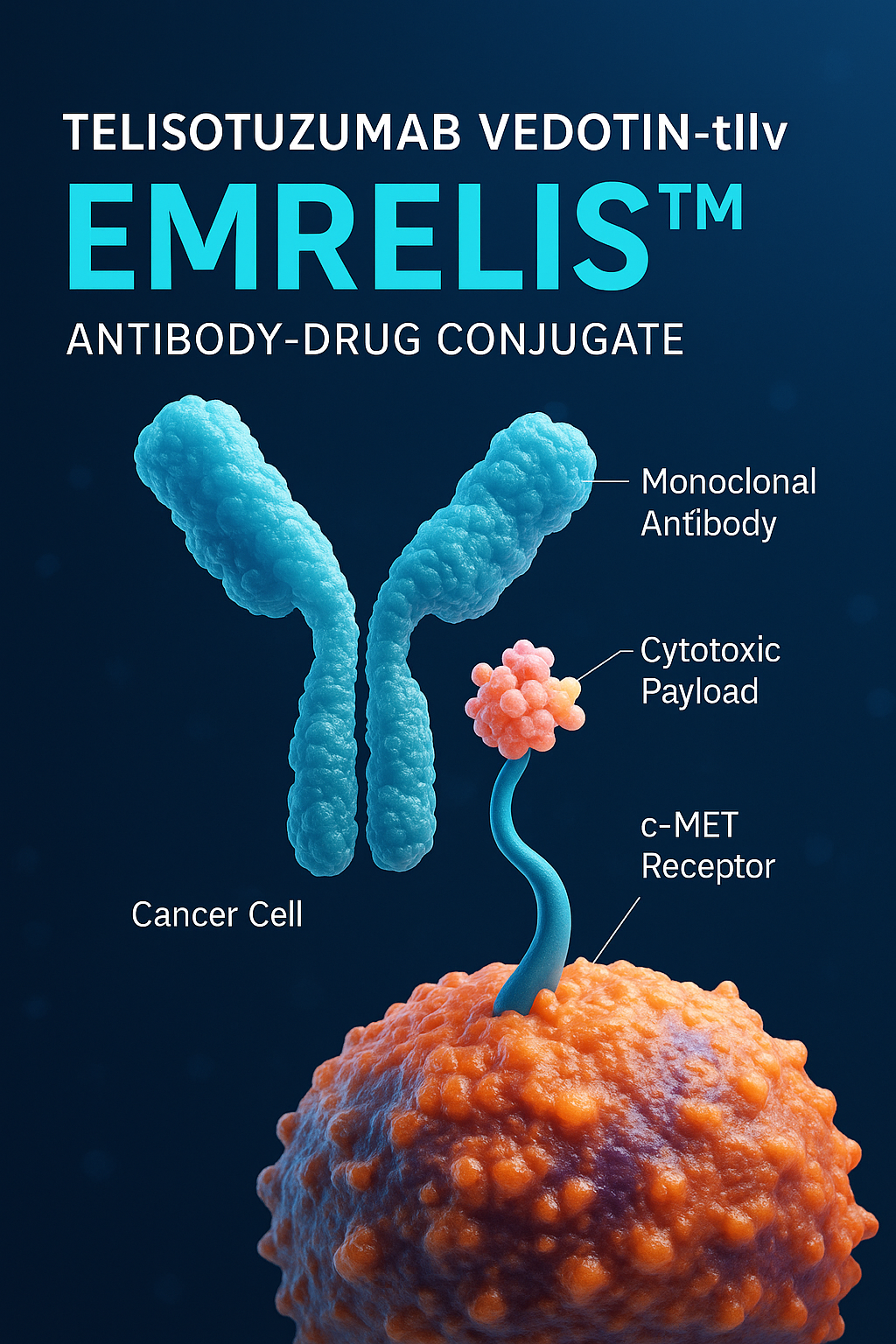
Telisotuzumab vedotin-tllv is a type of antibody-drug conjugate (ADC). It works by combining a monoclonal antibody targeting c-MET with a potent chemotherapy payload, monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE). This design allows the drug to deliver its cytotoxic payload directly into cancer cells, thereby minimizing damage to healthy tissues and increasing treatment precision.
The FDA’s accelerated approval was based on promising data from clinical trials demonstrating notable tumor responses, especially in patients with high c-MET expression. This makes EMRELIS™ a targeted therapy breakthrough, aligning with the broader movement toward precision oncology—treatments tailored to specific molecular characteristics of a patient’s tumor.
With its unique mechanism and focus on a high-risk subset of lung cancer patients, Telisotuzumab vedotin-tllv is poised to fill a critical gap in cancer care and may pave the way for broader applications of ADCs in solid tumors.
How Telisotuzumab Vedotin-tllv Works: Mechanism of Action Explained
Telisotuzumab vedotin-tllv (EMRELIS™) is a novel antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) designed to precisely target and kill cancer cells that overexpress the c-MET receptor, a protein frequently upregulated in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Its mechanism of action leverages the strength of targeted immunotherapy combined with potent cytotoxic chemotherapy, minimizing harm to healthy tissues while enhancing anti-tumor efficacy.
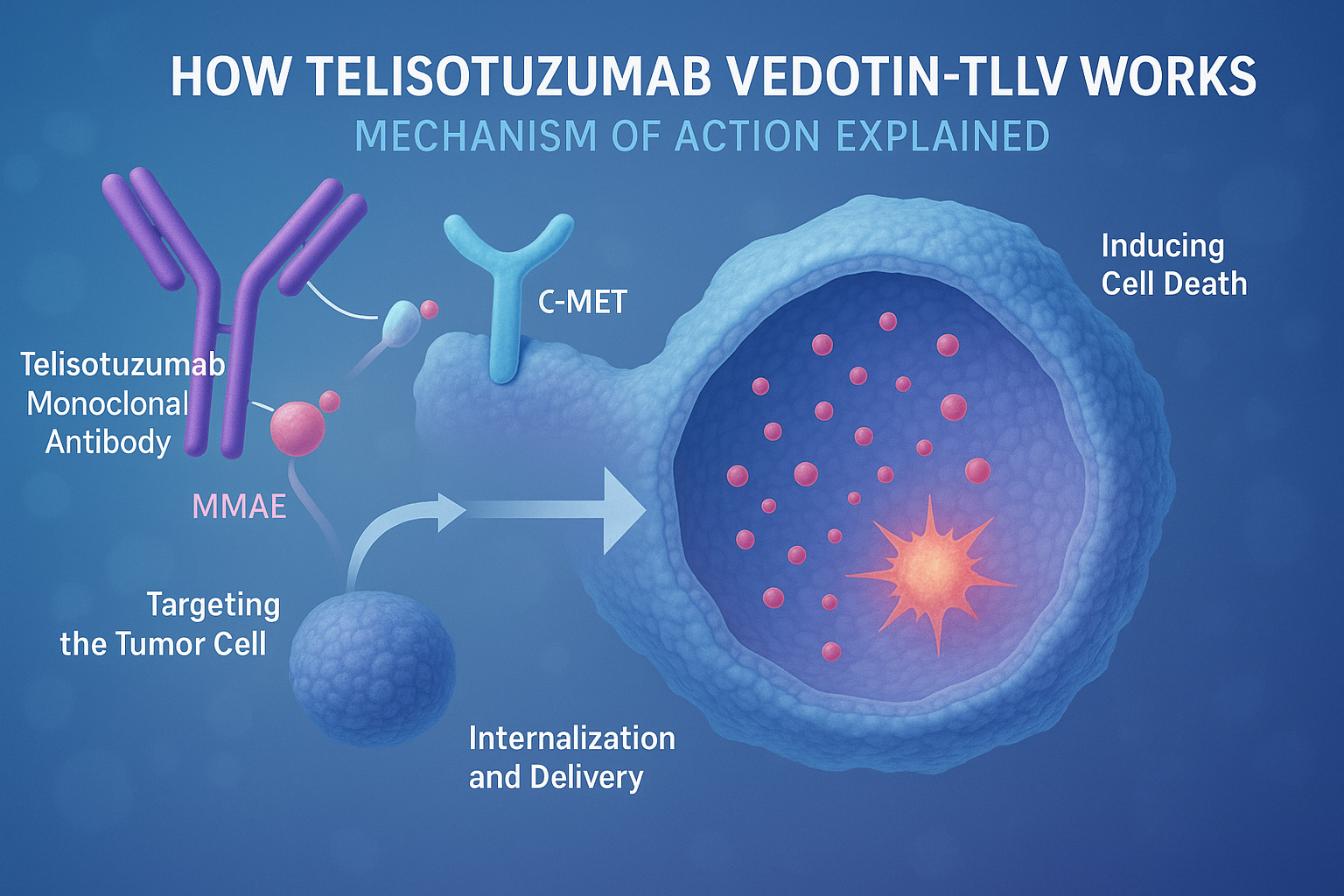
At the core of this therapy is telisotuzumab, a monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to the c-MET receptor on the surface of tumor cells. This antibody is chemically linked to monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), a powerful antimitotic agent that disrupts microtubules—structures essential for cell division. Once telisotuzumab binds to c-MET, the entire ADC is internalized by the cancer cell through receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Inside the tumor cell, enzymatic processes cleave the linker, releasing MMAE into the cytoplasm. The released MMAE binds to tubulin and disrupts microtubule polymerization, causing cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase and ultimately leading to apoptosis or programmed cell death.
This selective delivery system is what distinguishes EMRELIS™ from traditional chemotherapy. Because MMAE is only released inside c-MET–expressing cells, the surrounding healthy tissues are largely spared, thereby reducing systemic toxicity. This targeted approach represents a significant evolution in the treatment of advanced NSCLC, particularly for patients whose tumors exhibit high c-MET expression, often associated with poor prognosis and resistance to standard therapies.
In summary, Telisotuzumab vedotin-tllv offers a precision-based therapeutic mechanism that maximizes cancer cell destruction while minimizing collateral damage—a hallmark of next-generation oncology drugs.
Who is it For? FDA-Approved Indication & Patient Eligibility
Telisotuzumab vedotin-tllv (EMRELIS™) was granted accelerated approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in May 2025 for the treatment of adults with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors overexpress c-MET, and who have progressed on or after prior systemic therapy. This approval marks a significant advancement in addressing a critical unmet need in the lung cancer treatment landscape.
c-MET, short for “mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor,” is a proto-oncogene encoding a receptor tyrosine kinase involved in tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis. Approximately 25–30% of NSCLC cases show c-MET overexpression, which is associated with poor prognosis, increased metastatic potential, and resistance to standard therapies, including EGFR inhibitors.
To be eligible for treatment with EMRELIS™, patients must undergo biomarker testing to confirm elevated c-MET expression, usually determined by immunohistochemistry (IHC) or other validated assays. Patients with prior exposure to platinum-based chemotherapy or immune checkpoint inhibitors may especially benefit, as telisotuzumab vedotin offers a non-cross-resistant mechanism of action.
The treatment is not currently indicated for first-line therapy, nor for patients without confirmed c-MET overexpression. However, ongoing clinical trials may expand its indications to broader patient populations in the future.
Overall, EMRELIS™ introduces a precision-medicine option for a subset of NSCLC patients historically underserved by conventional therapies, emphasizing the growing role of biomarker-driven oncology.
Clinical Trial Results & Safety Profile
The FDA’s accelerated approval of Telisotuzumab vedotin-tllv (EMRELIS™) was primarily based on encouraging outcomes from multiple clinical trials, most notably the LUMINOSITY study—a phase II, multicenter, open-label trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of this targeted ADC in patients with c-MET–positive NSCLC.
In the study, patients with high c-MET expression demonstrated a confirmed objective response rate (ORR) of approximately 53%, with disease control rates exceeding 80%. Importantly, the therapy showed consistent efficacy across different subgroups, including those previously treated with chemotherapy and immunotherapy. The median progression-free survival (PFS) was reported at around 6.9 months, while overall survival (OS) was still maturing at the time of publication.
Beyond its efficacy, telisotuzumab vedotin has a manageable safety profile. The most frequently observed adverse events are characteristic of MMAE-based ADCs, including:
Peripheral neuropathy
Fatigue
Nausea
Neutropenia
Alopecia
While the majority of these adverse events are Grade 1 or 2, dose modifications were occasionally required in patients with more severe neuropathy or hematologic toxicities.
No new safety signals emerged during clinical development, and the risk-benefit profile was deemed favorable—especially in a population with limited treatment options and poor outcomes with existing therapies.
Overall, the trial results support EMRELIS™ as a promising option in the treatment arsenal for c-MET–positive NSCLC, reinforcing the value of ADCs in solid tumors with defined molecular targets.
What’s Next: Future Directions, Trials, and Patient Access
Following its FDA accelerated approval in May 2025, Telisotuzumab vedotin-tllv (EMRELIS™) is now being positioned as a cornerstone therapy in the precision oncology landscape for c-MET–positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, its journey is far from over. Researchers and clinicians are actively exploring expanded indications, new combinations, and real-world access strategies to maximize its impact.
Currently, ongoing clinical trials are assessing the efficacy of EMRELIS™ in:
Earlier lines of treatment, including first-line settings for treatment-naïve patients
Combination regimens with immune checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., anti-PD-1/PD-L1) or chemotherapy
Other c-MET–driven cancers, such as gastric, head and neck, and papillary renal cell carcinoma
These studies aim to validate EMRELIS™ beyond its initial niche and evaluate whether broader populations can benefit from c-MET targeting—even in tumors with intermediate MET expression or MET exon 14 skipping mutations.
On the accessibility front, the drug’s manufacturer, AbbVie, has launched support programs for patients, including co-pay assistance and access pathways through oncologist networks. However, because EMRELIS™ is a specialty drug, it may still face reimbursement hurdles in certain healthcare systems. Advocates stress the need for biomarker testing integration into diagnostic workflows to ensure eligible patients are identified early.
Looking forward, EMRELIS™ stands as an example of the power of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) in reshaping solid tumor treatment. As more ADCs gain regulatory momentum, EMRELIS™ may pave the way for personalized therapy portfolios tailored to biomarker-driven subtypes of lung and other cancers.
References
Blair HA. Telisotuzumab Vedotin: First Approval. Drugs. 2025 Jul 30. doi: 10.1007/s40265-025-02210-z. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40736649.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40736649/
Telisotuzumab vedotin (Emrelis) for non-small cell lung cancer. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2025 Aug 4;67(1734):e132-e133. doi: 10.58347/tml.2025.1734e. PMID: 40729441.