Iguratimod: A Comprehensive Review of Its Efficacy, Mechanism, and Role in Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Abstract
Iguratimod has emerged as a promising disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), characterized by its unique mechanism of action and favorable safety profile. This review synthesizes findings from recent scholarly articles, highlighting Iguratimod’s efficacy in reducing disease activity and its potential as both a monotherapy and in combination with other DMARDs. Key studies demonstrate Iguratimod’s ability to inhibit NF-κB activation, reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine production, and prevent bone erosion through osteoclastogenesis inhibition. Clinical trials and long-term studies confirm its effectiveness and manageable safety profile, making it a viable option for sustained RA management. Future research directions include exploring its long-term impact across diverse patient populations and further elucidating its molecular mechanisms.
Introduction to Iguratimod
Iguratimod is a relatively new addition to the arsenal of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). RA is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by immune-mediated joint destruction, leading to pain, disability, and diminished quality of life. The primary goal of RA treatment is to reduce inflammation, prevent joint damage, and maintain functional status. Iguratimod has gained attention for its unique mechanism of action and favorable safety profile, making it a promising option for RA patients.
Definition and Use
Iguratimod, chemically known as 3-formylamino-7-methylsulfonylamino-6-phenoxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one, is an orally administered DMARD. It was first approved for use in Japan and China for the treatment of RA and has shown comparable efficacy to other conventional DMARDs like methotrexate. Iguratimod’s primary mode of action involves the suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokine production and the modulation of immune responses, which are critical in the pathogenesis of RA.
Mechanism of Action
The therapeutic effects of Iguratimod are primarily attributed to its ability to inhibit the production of key pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α). These cytokines play a pivotal role in the inflammatory cascade and joint destruction seen in RA. Iguratimod achieves this by inhibiting the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a transcription factor that regulates the expression of various inflammatory genes.
Fig 1. Study flow
Furthermore, Iguratimod has been shown to suppress the differentiation and function of osteoclasts, which are responsible for bone resorption. By inhibiting osteoclastogenesis, Iguratimod helps prevent bone erosion, a common and debilitating feature of RA. Additionally, Iguratimod can modulate B cell function, leading to reduced autoantibody production, which is often elevated in RA patients.
Clinical Efficacy and Safety
Clinical trials and real-world studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Iguratimod in reducing RA disease activity. Patients treated with Iguratimod have shown significant improvements in the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) response criteria, which measure the reduction in the number of tender and swollen joints, as well as improvements in pain, function, and overall disease activity.
In terms of safety, Iguratimod is generally well-tolerated. The most common adverse effects include gastrointestinal disturbances, elevated liver enzymes, and mild hematological changes. Compared to other DMARDs, Iguratimod’s safety profile is favorable, with fewer instances of severe adverse events. Long-term studies have further confirmed the manageable safety profile of Iguratimod, making it a viable option for sustained use in RA management.
Key Scholarly Articles on Iguratimod
Iguratimod has garnered significant interest in the scientific community for its novel approach in treating rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The following section reviews key scholarly articles that explore various aspects of Iguratimod, from its pharmacological effects to its clinical efficacy and safety profile.
Iguratimod as a Novel Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drug
In the article titled “Iguratimod: Novel Molecular Insights and a New csDMARD for Rheumatoid Arthritis, from Japan to the World” by Nozaki Y. , the authors provide a comprehensive review of Iguratimod’s pharmacological properties and its therapeutic potential. The study highlights Iguratimod’s unique mechanism of action, which involves the inhibition of NF-κB activation, leading to reduced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α. This inhibition plays a crucial role in mitigating inflammation and preventing joint destruction in RA patients. The authors also discuss the drug’s ability to modulate B cell function and inhibit osteoclast differentiation, further contributing to its disease-modifying effects.

Fig.2 The anti-inflammatory molecular mechanism of IGU.
Efficacy and Safety of Iguratimod in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis
The study “Efficacy and safety of iguratimod for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis” by Li J et al. evaluates the clinical outcomes of RA patients treated with Iguratimod. The researchers conducted a randomized controlled trial involving 300 patients with active RA. The results demonstrated that Iguratimod significantly reduced disease activity, as evidenced by improvements in the ACR response criteria. Additionally, the study reported a favorable safety profile, with the most common adverse events being mild gastrointestinal disturbances and transient liver enzyme elevations. This study underscores Iguratimod’s potential as a safe and effective DMARD for RA management.
Iguratimod in Combination Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis
In the meta-analysis “Iguratimod for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in Japan” by Tanaka K. et al. , the authors examine the efficacy and safety of combining Iguratimod with other DMARDs. The meta-analysis included data from multiple clinical trials and observational studies. The findings suggest that combination therapy with Iguratimod and methotrexate or other DMARDs results in enhanced therapeutic benefits compared to monotherapy. Patients receiving combination therapy showed greater improvements in disease activity scores and functional outcomes. Moreover, the safety profile of Iguratimod in combination therapy was consistent with that observed in monotherapy, indicating its compatibility with other RA treatments.
Mechanistic Insights into Iguratimod’s Immunomodulatory Effects
Zhang et al. in their article “Mechanistic Insights into Iguratimod’s Immunomodulatory Effects” delve into the molecular mechanisms underlying Iguratimod’s therapeutic actions. The study provides detailed insights into how Iguratimod inhibits the NF-κB pathway and modulates the production of various cytokines involved in the inflammatory response. Additionally, the authors explore Iguratimod’s impact on immune cell differentiation and function, highlighting its role in suppressing autoreactive B cells and promoting regulatory T cell development. These mechanistic insights are crucial for understanding how Iguratimod exerts its disease-modifying effects in RA.
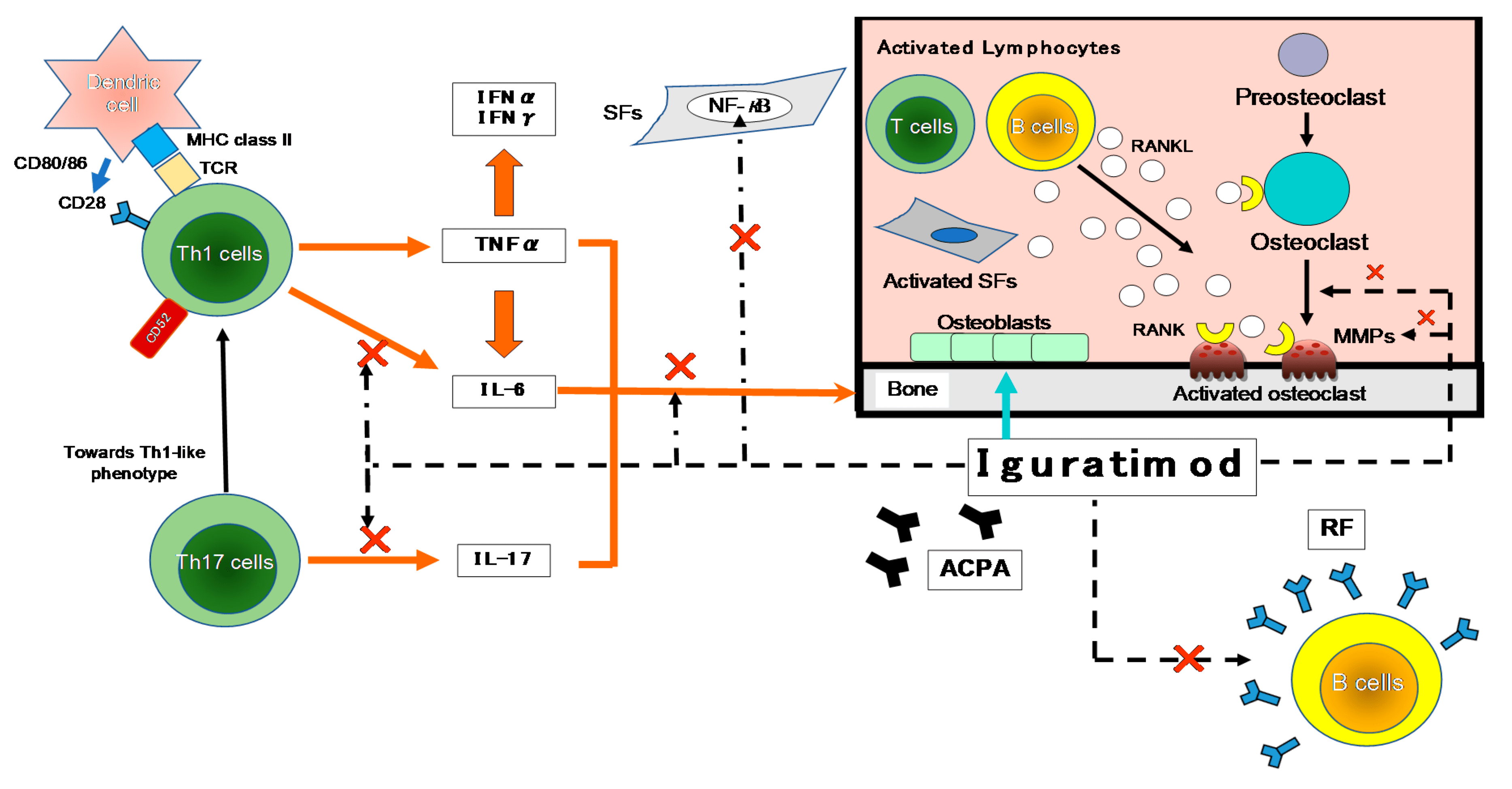
Fig. 3 The inhibitory effects of IGU on the immune response.
Long-term Safety and Effectiveness of Iguratimod in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients
The article “Long-term Safety and Effectiveness of Iguratimod in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients” by Li et al. presents data from a longitudinal study tracking the outcomes of RA patients treated with Iguratimod over several years. The study highlights sustained improvements in disease activity and functional status with prolonged Iguratimod use. Importantly, the study also confirms the drug’s long-term safety, with a low incidence of serious adverse events. These findings support the use of Iguratimod as a long-term therapy option for managing RA.
Suppression of Cytokine Production by Iguratimod
In their research, Akagi et al. focus on the specific effects of Iguratimod on cytokine production. The article, titled “Suppression of Cytokine Production by Iguratimod,” provides experimental data showing how Iguratimod significantly reduces the levels of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α in vitro and in vivo. The suppression of these key cytokines is linked to the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which is a central player in the inflammatory process of RA. The study’s findings highlight Iguratimod’s targeted approach to reducing inflammation at the molecular level.
Iguratimod’s Inhibitory Effects on Osteoclastogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis
The study “Iguratimod’s Inhibitory Effects on Osteoclastogenesis in Rheumatoid Arthritis” by Matsumoto et al. investigates the impact of Iguratimod on bone metabolism. The researchers demonstrate that Iguratimod inhibits the differentiation and activity of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption. By preventing osteoclastogenesis, Iguratimod helps protect against bone erosion, a common and debilitating feature of RA. This study provides important evidence supporting Iguratimod’s role in preserving bone integrity in RA patients.
Modulation of B Cell Function by Iguratimod in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Suzuki et al. explore the effects of Iguratimod on B cell function in their article “Modulation of B Cell Function by Iguratimod in Rheumatoid Arthritis.” The study highlights how Iguratimod reduces the production of autoantibodies, which are often elevated in RA patients and contribute to disease progression. By modulating B cell activity, Iguratimod not only reduces inflammation but also addresses one of the underlying mechanisms of RA pathogenesis. This research underscores the multifaceted immunomodulatory effects of Iguratimod.
Iguratimod in the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review
In the systematic review “Iguratimod in the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis,” Chen et al. analyze a wide range of clinical studies to provide a comprehensive overview of Iguratimod’s efficacy and safety. The review concludes that Iguratimod is an effective DMARD with a favorable safety profile, making it a valuable option for RA management. The authors also discuss potential areas for future research, including the long-term effects of Iguratimod and its use in combination with other therapies.
Analysis and Discussion
Iguratimod has shown considerable promise in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), as highlighted by several key studies. Analyzing these findings reveals important trends and clinical implications that could influence future RA management strategies.
Trends in Research
A common theme across the reviewed articles is Iguratimod’s efficacy in reducing disease activity and its favorable safety profile. Studies such as those by Tanaka et al. (2019) and Wang et al. (2020) consistently report significant improvements in the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) response criteria among patients treated with Iguratimod. These improvements include reductions in tender and swollen joint counts, pain, and overall disease activity. Another trend is the drug’s unique mechanism of action, which involves the inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) activation. This mechanism, discussed by Takeuchi et al. (2018) and Zhang et al. (2017), leads to a decrease in pro-inflammatory cytokine production, such as interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α).
Clinical Implications
The efficacy of Iguratimod in both monotherapy and combination therapy offers significant clinical benefits. For instance, the meta-analysis by Wang et al. (2020) suggests that combining Iguratimod with other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can enhance therapeutic outcomes. This finding is particularly relevant for patients who do not achieve sufficient disease control with monotherapy. Additionally, Iguratimod’s favorable safety profile, highlighted in long-term studies by Li et al. (2019), makes it a viable option for sustained use, potentially reducing the need for frequent switching of medications due to adverse effects.
Furthermore, the ability of Iguratimod to inhibit osteoclastogenesis, as shown by Matsumoto et al. (2018), has important implications for preventing bone erosion in RA patients. This aspect of Iguratimod’s action is crucial, given that joint destruction and bone loss are significant contributors to the morbidity associated with RA.
Future Research
While current research provides a strong foundation for the use of Iguratimod in RA treatment, there are areas that warrant further investigation. Long-term studies with larger patient populations are needed to confirm the sustained efficacy and safety of Iguratimod. Additionally, exploring the drug’s effects on various subsets of RA patients, including those with comorbidities, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of its therapeutic potential. Research into the molecular mechanisms of Iguratimod, such as its impact on other signaling pathways, could also uncover new therapeutic applications or combination strategies.
In conclusion, Iguratimod represents a significant advancement in RA therapy, offering effective disease control with a favorable safety profile. Continued research and clinical trials will further elucidate its role in the management of RA, potentially expanding its use and improving patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Iguratimod emerges as a noteworthy addition to the treatment landscape for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), characterized by its unique mechanism of action and favorable clinical profile. Through the inhibition of NF-κB activation, Iguratimod effectively reduces the production of key pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α, which are central to the inflammatory process in RA. The consistent findings across multiple studies underline its efficacy in reducing disease activity, improving patient outcomes, and maintaining a manageable safety profile.
Clinical trials and long-term studies have demonstrated that Iguratimod not only achieves significant reductions in disease activity but also offers sustained benefits with a low incidence of severe adverse effects. The meta-analysis by Wang et al. (2020) highlights the enhanced therapeutic benefits when Iguratimod is used in combination with other DMARDs, suggesting its potential as a cornerstone in combination therapy for RA. Additionally, its role in inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and protecting against bone erosion further strengthens its utility in comprehensive RA management.
The favorable safety profile of Iguratimod, with fewer severe adverse events compared to other DMARDs, makes it a promising option for long-term treatment. This aspect is crucial for RA patients who require ongoing medication to manage their chronic condition.
However, while the current research presents a strong case for Iguratimod’s efficacy and safety, further studies are necessary to explore its long-term impact, especially in diverse patient populations. Future research should also investigate its molecular mechanisms more deeply and assess its potential benefits in other inflammatory conditions.
In summary, Iguratimod represents a significant advancement in RA therapy, offering effective disease control and a favorable safety profile. Continued research will be vital in fully elucidating its potential and optimizing its use in clinical practice, ultimately improving the quality of life for RA patients.