How to Treat Depression in Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors?
Abstract
Talking about depression is frightening and not new to everyone. In the current era of rapid development, depression is now the most common type of psychological disorder, with continuous and prolonged depressed mood as the main clinical feature, and is the most important type of psychological disorder in the modern age. Depression is a type of depressive disorder (depressive disorder also includes poor mood) and is a chronic relapsing disorder with symptoms including depressed mood, reduced interest, delayed thinking, reduced attention and memory, self-denial, poor appetite, and reduced activity. The prevalence of depression is on the rise, and now depression has become the fourth most common disease in the world’s disease list, with a conservative estimate of 350 million depressed people worldwide, and 10-15% of depressed people eventually die by suicide.
Introduction
For the treatment of depression, its monoamine oxidase inhibitor drugs can occupy a place. Many people are more aware of monoamine oxidase inhibitors are an enzyme with selective metabolism, monoamine oxidase inhibitors have an effect on the human stomach and liver, monoamine oxidase inhibitors require extra attention in the process of use because monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and many drugs can cause discomfort if used together.
Many drugs are monoamine oxidase inhibitors. For example, phenelzine, isoniazid, isopropyl hydrazine, phencyclidine, moclobemide, brodifacoum, cyanamide, toloxadone, and deferoxamine for depression; sildenafil for Parkinson’s disease; and eugenol (consisting mainly of procaine, inositol, and vitamin B6) for hypertension. Notably, certain herbs also have monoamine oxidase inhibitory effects, such as indigo, deer antler, hawthorn, and he shou wu.
What are monoamine oxidase inhibitors?
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) was the first antidepressant discovered and was once widely used in psychiatry. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors include isoniazid, isopropyl hydrazine, phenisopropylhydrazine, phenelzine, isocarbohydrazide, and other drugs. Monoamine oxidase itself is a naturally occurring enzyme in the body that catalyzes monoamines and performs oxidative deamination reactions. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, on the other hand, reduce the destruction of monoamine transmitters in the central nervous system, increase the concentration in the synaptic gap, and improve mood by inhibiting the heterogeneous physiological activity of monoamine oxidase. It can alleviate or eliminate diseases caused by the reduction of monoamines from various causes, or by the excessive activity of monoamine oxidase.
Mechanism of action of monoamine oxidase inhibitors
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors act by inhibiting monoamine oxidase activity, thereby preventing the breakdown of monoamine neurotransmitters and thus increasing their availability. There are two isoforms of monoamine oxidase, MAO-A and MAO-B. MAO-A preferentially deaminates serotonin, melatonin, epinephrine, and norepinephrine. MAO-B preferentially deaminates phenylethylamine and certain trace amines; in contrast, MAO-A preferentially deaminates other trace amines, such as tyramine, while dopamine is equally deaminated by both types.
The following is a brief description of the uses of several monoamine oxidase inhibitors.
What are the uses of isoniazid?
Isoniazid, also known as a 4-pyridinecarbohydrazide and isonicotinic acid hydrazide, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H7N3O, a hydrazide of isonicotinic acid, which is a white crystalline powder and is a first-line anti-tuberculosis drug together with rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide.
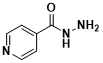
The structural formula of isoniazid (Figure 1)
Isoniazid inhibits and kills Mycobacterium tuberculosis, has good biofilm penetration, and is classified as the antagonist of choice because of its efficacy, low toxicity, low cost, and ease of oral administration.
Isoniazid was also the first antidepressant but was withdrawn from the market because of strong hepatotoxicity
Isoniazid is highly selective for Mycobacterium tuberculosis and has a strong antibacterial effect. Concentrations of 0.025~0.05 mg/L in test tubes can inhibit bacteria, and the higher concentration of 10 mg/L has a bactericidal effect on bacteria in the reproductive phase. For resting Mycobacterium tuberculosis, increasing the concentration of the drug or extending the contact time also has a bactericidal effect. It has the same killing effect on Mycobacterium tuberculosis inside and outside the cell. Isoniazid alone is susceptible to drug resistance. Combining the drugs can delay the development of resistance and enhance efficacy. There is no cross-resistance between isoniazid and other anti-tuberculosis drugs.
Isoniazid is clinically the drug of choice for the treatment of tuberculosis and is indicated for various types of tuberculosis, such as pulmonary, lymphatic, bone, renal and intestinal tuberculosis, tuberculous meningitis, pleurisy, and peritonitis. To prevent and alleviate the development of drug resistance, it should be used in combination with other first-line anti-tuberculosis drugs.
What are the uses of phenelzine sulfate?
Phenelzine sulfate is an organic compound, a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) with the chemical formula C8H14N2O4S. It is mainly used clinically to treat depression and relieve angina pectoris.
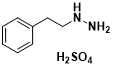
The structural formula of phenelzine sulfate (Figure 2)
Phenelzine sulfate for the treatment of depression, especially reactive depression.
Phenelzine sulfate for the treatment of phobias and depressive neurosis
Phenelzine sulfate is used for the treatment of episodic sleeping sickness and the relief of angina pectoris.
What are the uses of isocarbohydrazide?
Isocarbohydrazide is a non-selective, irreversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase with an IC50 value of 4.8 μM measured in rat brains and a chemical formula of C12H13N3O2.
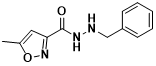
The structural formula of isocarbohydrazide (Figure 3)
Isocarbohydrazide acts as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor class of antidepressants. It produces irreversible binding with monoamine oxidase A and B in the brain and affects the metabolism of monoamine neurotransmitters. The inhibition of monoamine oxidase increases the content of monoamines (mainly norepinephrine and 5-hydroxytryptamine) in the central nervous system and exerts an antidepressant effect.
Isocarbohydrazide is mainly used in patients with depression in which tricyclic antidepressants are ineffective. It is effective in depression with symptoms of anxiety and hypochondriasis.
What are the uses of isoproterenol?
Isoprostanolide is an antidepressant drug introduced in the 1950s. Isoproterenol was originally an anti-tuberculosis drug, so it acts as a central stimulant for hyperactivity, talkativeness, insomnia, and euphoria. It was first used with success in 1957 to treat depressed patients. Animal experiments demonstrated that isoproterenol reversed the hyperkinetic and apathetic effects caused by reserpine and increased brain monoamine levels in depressed patients. The central excitatory and antidepressant effects of isoproterenol are due to a decrease in the degradation of monoamines due to the inhibition of monoamine oxidase in the brain, increasing synaptic gap nonreceptor levels.
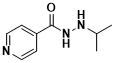
The structural formula of isopropyl hydrazine (Figure 4)
Summary
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors, an older antidepressant, have also been used quite effectively in depression. Then, the next step will be to realize how to achieve the new use of the old drug of monoamine oxidase inhibitor to maximize its efficacy to benefit.
References
- Bhawna, Kumar A, Bhatia M, Kapoor A, Kumar P, Kumar S. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors: A concise review with special emphasis on structure activity relationship studies. Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Nov 15;242:114655. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114655. Epub 2022 Aug 18. PMID: 36037788.
- Duarte P, Cuadrado A, León R. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors: From Classic to New Clinical Approaches. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021;264:229-259. doi: 10.1007/164_2020_384. PMID: 32852645.
- Sub Laban T, Saadabadi A. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI). 2022 Jul 19. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan–. PMID: 30969670.
- Grabowski Ł. Inhibitory monoaminooksydazy (IMAO): farmakologia, metabolizm i zastosowanie w terapii depresji o różnej etiologii [Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI): pharmacology, metabolism and application in the treatment of depression]. Postepy Biochem. 2021 May 25;67(2):130-140. Polish. doi: 10.18388/pb.2021_382. PMID: 34378889.
- Jiang Y, Li Y, Liu C, Zhang L, Lv D, Weng Y, Cheng Z, Chen X, Zhan J, Zhang H. Isonicotinylation is a histone mark induced by the anti-tuberculosis first-line drug isoniazid. Nat Commun. 2021 Sep 20;12(1):5548. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25867-y. PMID: 34545082; PMCID: PMC8452692.
- Beechinor RJ, Tyson R, Roth ME. Phenelzine and Morphine Drug-Drug Interaction? A Literature Review. J Pharm Pract. 2021 Oct;34(5):818-823. doi: 10.1177/0897190020970752. Epub 2020 Dec 3. PMID: 33267714.