Ceramides: The Secret to Stronger, Healthier Skin Barrier
Abstract
Ceramides are essential lipid molecules naturally found in the skin, playing a critical role in maintaining hydration, protecting the barrier function, and supporting overall skin health. This article explores what ceramides are, their biological structure, and how they function within the epidermis. It outlines the benefits of ceramides for various skin types, especially those prone to dryness, sensitivity, and aging. Readers will also learn how to effectively use ceramide-enriched skincare products and determine whether ceramides suit their skin needs. With support from scientific literature, this blog provides a comprehensive yet accessible guide to incorporating ceramides into a modern skincare routine.
What Is Ceramide? A Skincare Essential You Should Know
If you’ve ever struggled with dry, irritated, or aging skin, chances are your skincare routine is missing one crucial ingredient: ceramide. Often overlooked but highly effective, ceramides are naturally occurring lipid molecules (fats) found in the outermost layer of the skin — the stratum corneum. They play a fundamental role in maintaining a healthy skin barrier and locking in moisture.
In simpler terms, ceramides act like the “mortar” between the “bricks” of your skin cells. They hold everything together, sealing the skin’s surface to prevent moisture loss and block out harmful environmental irritants like pollutants, bacteria, and allergens. Without enough ceramides, the skin becomes dry, inflamed, and more prone to damage.
Naturally present in the skin, ceramide levels decline as we age or due to environmental exposure (such as harsh cleansers, UV radiation, and low humidity). This depletion is a common cause of barrier dysfunction, which can lead to eczema, psoriasis, and accelerated aging.
Luckily, many skincare products today include bio-identical ceramides that mimic your skin’s own lipids. These are often combined with other hydrators like hyaluronic acid or niacinamide to enhance effectiveness. Whether you have dry skin or simply want to strengthen your skin’s defenses, incorporating ceramides into your skincare routine is a smart and science-backed choice.
The Science Behind Ceramides
Ceramides are sphingolipids, a class of fat molecules composed of a sphingosine base linked to a fatty acid. They are primarily located in the stratum corneum, the skin’s outermost layer, where they represent nearly 50% of the skin’s lipid content by weight. Together with cholesterol and free fatty acids, ceramides form a tightly packed lamellar structure that is essential for skin barrier integrity.
Ceramides are not just passive structural lipids—they also participate in cellular signaling. Inside cells, they regulate critical biological processes including inflammation, apoptosis, and cell differentiation. Disruptions in ceramide metabolism are linked to skin disorders (e.g., atopic dermatitis) and systemic conditions like insulin resistance and neurodegenerative diseases.
Ceramide levels in the skin can decline with aging, UV exposure, and the use of harsh cleansing agents. This breakdown compromises the skin’s defense system and leads to dryness, sensitivity, and premature aging. Fortunately, topical application of bio-identical or synthetic ceramides can replenish the skin’s natural stores and restore healthy function.
Benefits of Ceramides for Skin
Ceramides are vital to achieving and maintaining healthy, resilient skin. As key components of the skin barrier, they help form a waterproof seal that prevents transepidermal water loss (TEWL) and shields the skin from environmental aggressors like pollution, irritants, and allergens.
One of their most notable benefits is hydration. Ceramides bind skin cells together and retain moisture, making them especially beneficial for dry or dehydrated skin. In individuals with eczema, psoriasis, or sensitive skin, ceramide levels are often significantly reduced, resulting in barrier disruption and inflammation. Supplementing with topical ceramides helps restore barrier function, reduce redness, and improve skin smoothness.

Additionally, ceramides can enhance the effectiveness of other active ingredients, such as niacinamide and hyaluronic acid, when used together in formulations. This synergistic action improves skin tone, elasticity, and reduces signs of premature aging, such as fine lines and rough texture.
Ceramide-based products are generally non-comedogenic and suitable for most skin types, including acne-prone and sensitive skin, making them a cornerstone in dermatology and everyday skincare routines.
How to Use Ceramides in Your Skincare Routine
Incorporating ceramides into your skincare routine is both simple and highly effective. Ceramide-rich products come in many forms — cleansers, moisturizers, serums, eye creams, and even barrier-repair ointments. Choosing the right type depends on your skin’s needs and the overall routine structure.
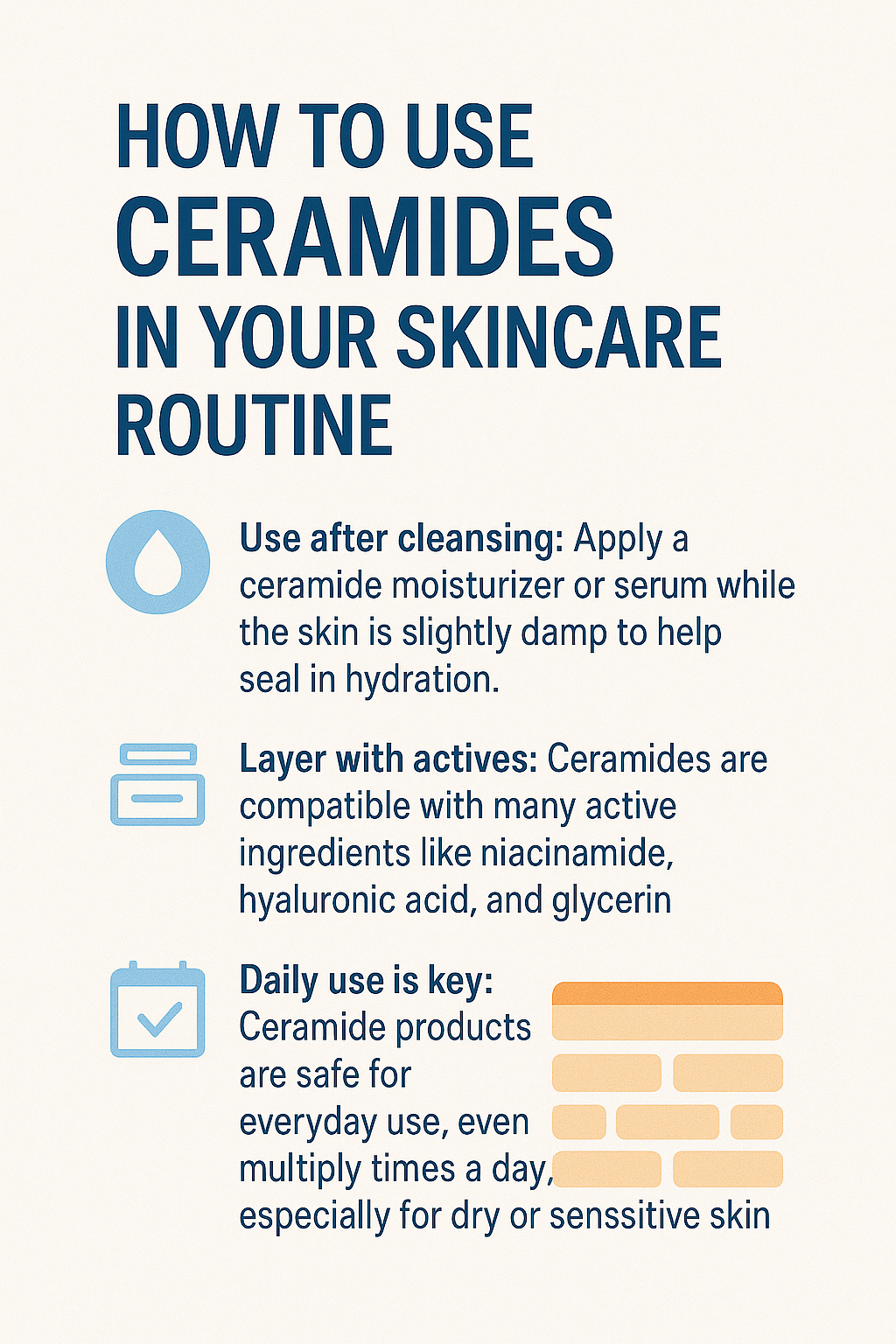
To get the most out of ceramides:
Use after cleansing: Apply a ceramide moisturizer or serum while the skin is slightly damp to help seal in hydration.
Layer with actives: Ceramides are compatible with many active ingredients like niacinamide, hyaluronic acid, and glycerin — all of which improve barrier health when combined.
Daily use is key: Ceramide products are safe for everyday use, even multiple times a day, especially for dry or sensitive skin.
For acne-prone or oily skin, opt for lightweight or gel-based ceramide formulations that won’t clog pores. If you’re using exfoliants (like AHAs, BHAs, or retinoids), ceramides can buffer irritation and support the skin’s healing process.
Lastly, consistency matters — regular use strengthens your barrier, improves texture, and reduces sensitivity over time.
Is Ceramide Right for You?
Whether you’re dealing with dry patches, sensitive skin, or just want to future-proof your skincare routine, ceramides are a safe and effective choice for nearly everyone. Because they are bio-identical to the lipids naturally found in human skin, ceramides are well-tolerated, even by those with eczema, rosacea, or acne-prone skin.
Ceramide-enriched products are particularly helpful for:
People with compromised skin barriers (from over-exfoliation or environmental damage)
Individuals experiencing seasonal dryness
Aging skin, as ceramide levels naturally decline with age
However, not all ceramide products are created equal. Look for formulations that list ceramide NP, AP, EOP, or EOS near the top of the ingredient list, ideally combined with cholesterol and fatty acids, which work synergistically for optimal barrier repair.
If your skin often feels tight, flaky, or reactive, adding ceramides could make a significant difference in just a few weeks. Long-term, they help prevent moisture loss, reduce sensitivity, and promote smoother, healthier skin texture.
In short: if you’re serious about skin health, ceramides deserve a top spot in your routine.
References
Elias, P. M. (2005). Stratum corneum defensive functions: An integrated view. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 125(2), 183–200.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022202X15323939
Bouwstra, J. A., & Ponec, M. (2006). The skin barrier in healthy and diseased state. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Biomembranes, 1758(12), 2080–2095.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0005273606002410
Madison, K. C. (2003). Barrier function of the skin: “La Raison d’Être” of the epidermis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 121(2), 231–241.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022202X15303560
van Smeden, J., Janssens, M., Gooris, G. S., & Bouwstra, J. A. (2014). The important role of stratum corneum lipids for the cutaneous barrier function. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1841(3), 295–313.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1388198113002485
Rawlings, A. V., & Harding, C. R. (2004). Moisturization and skin barrier function. Dermatologic Therapy, 17(s1), 43–48.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1396-0296.2004.04S1005.x