Berbamine Dihydrochloride: Nature’s Hidden Weapon Against Viruses and Cancer
Abstract
Berbamine dihydrochloride is a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid derived from Berberis species, known for its wide-ranging pharmacological effects. Recent scientific studies have highlighted its potential as an antiviral, anticancer, and autophagy-modulating agent. It has demonstrated promising activity against RNA viruses like SARS-CoV-2 and Mayaro virus, and shown the ability to inhibit tumor growth by targeting critical signaling pathways. Despite its benefits, concerns about compound mislabeling and safety underscore the need for high-purity sourcing and further clinical research. Although currently limited to laboratory use, berbamine dihydrochloride represents a powerful natural compound with significant potential in modern drug development and biomedical science.
What is Berbamine Dihydrochloride?
Berbamine dihydrochloride is a synthetic salt form of berbamine, a natural compound originally isolated from Berberis species, particularly Berberis amurensis. It belongs to a class of naturally occurring molecules known as bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids, which have been studied for their diverse biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and antiviral effects.
The dihydrochloride form enhances the solubility and stability of berbamine, making it more suitable for laboratory research and pharmaceutical testing. While berbamine itself has been explored for decades in traditional Chinese medicine, recent biomedical studies have revived interest in its molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential, especially in the context of viral infections and cancer.
What makes berbamine particularly intriguing is its multitargeted action. Research suggests that it may influence various cell signaling pathways, such as JAK/STAT, NF-κB, and autophagy-related proteins like BNIP3. This gives it a broad spectrum of potential applications in treating conditions ranging from leukemia to SARS-CoV-2 infections.
Berbamine dihydrochloride is currently available for research purposes only, and it is important to emphasize that it has not yet received approval for clinical or therapeutic use in humans. However, its promising in vitro and in vivo effects have made it a hot topic in pharmacological and biomedical research.
As the demand for plant-derived bioactives increases, berbamine dihydrochloride stands out as a compelling candidate for further exploration in modern drug development pipelines.
Key Pharmacological Properties of Berbamine Dihydrochloride
Berbamine dihydrochloride exhibits a wide range of pharmacological activities that make it a promising candidate in the field of drug discovery and disease treatment. Derived from the bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid family, it demonstrates strong bioactivity against cancer cells, viruses, and inflammatory pathways, making it a versatile tool in biomedical research.
One of the most studied properties of berbamine is its anticancer activity. It has shown the ability to inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis in various cancer cell lines, including leukemia, liver cancer, and breast cancer. This effect is believed to be mediated through inhibition of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway, a crucial mechanism in cell growth and immune regulation.
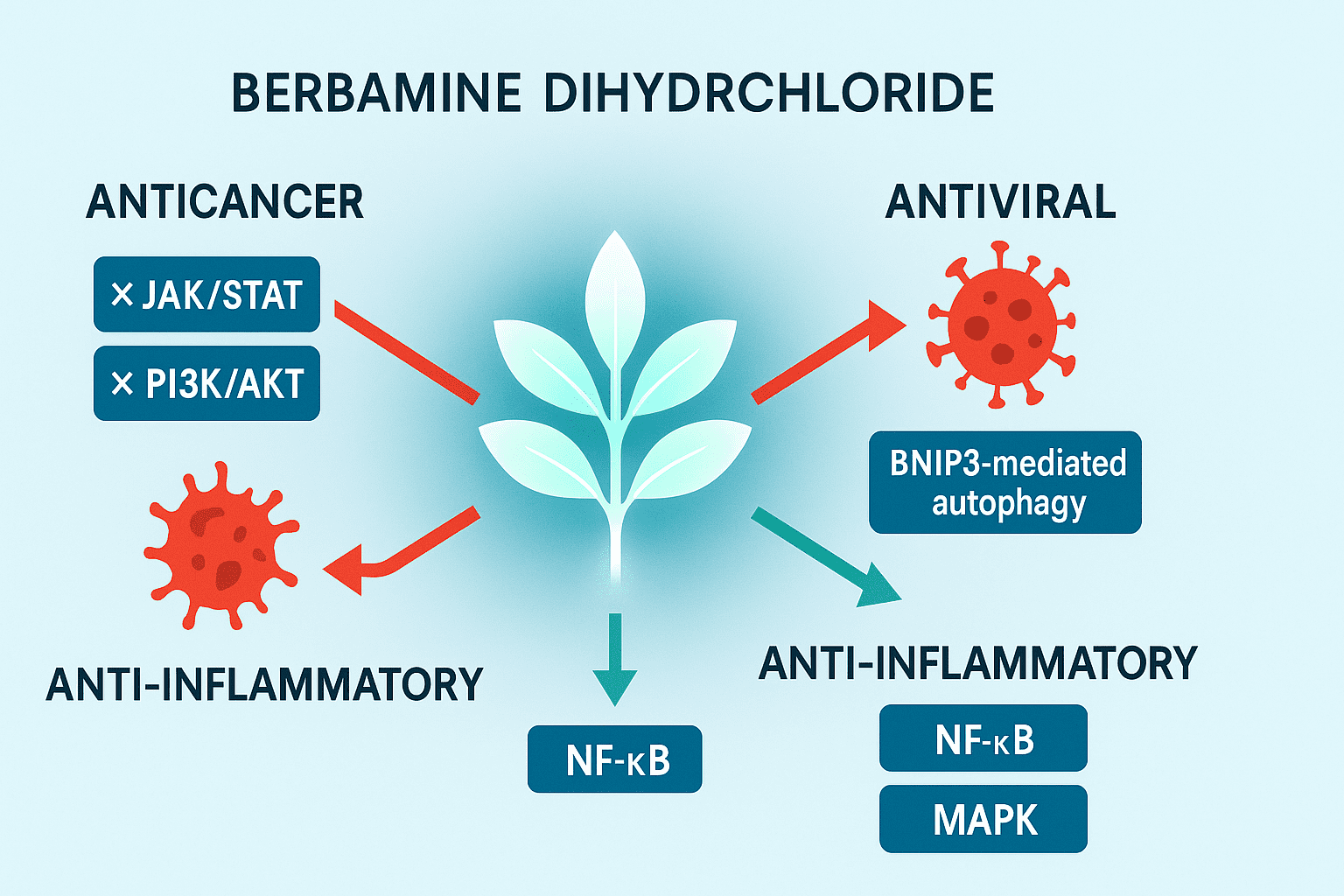
In addition to its anticancer effects, berbamine dihydrochloride is gaining attention for its antiviral activity. Recent studies suggest it may interfere with the replication cycle of RNA viruses, including Mayaro virus and SARS-CoV-2. One mechanism involves the inhibition of BNIP3-mediated autophagy, a cellular process that some viruses hijack to support their replication.
Moreover, berbamine has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects, potentially by downregulating NF-κB and MAPK pathways, which are involved in chronic inflammation and immune responses.
Importantly, most of these findings come from preclinical studies, primarily in vitro or in animal models. While the results are encouraging, more data from clinical trials is needed to confirm its therapeutic potential in humans.
Overall, the multitargeted nature of berbamine dihydrochloride makes it a unique compound worth deeper exploration in oncology, virology, and immunology.
Scientific Research Highlights on Berbamine Dihydrochloride
Scientific interest in berbamine dihydrochloride has surged in recent years due to its demonstrated potential across multiple disease models. Several peer-reviewed studies and preclinical experiments have provided insights into how this compound functions in viral inhibition, cancer suppression, and even drug mislabeling issues in the pharmaceutical supply chain.
One of the most striking studies comes from 2025, where researchers investigated the role of berbamine in SARS-CoV-2 infection. The compound was found to inhibit BNIP3-mediated autophagy, a mechanism the virus uses to replicate within intestinal epithelial cells. This led to significantly reduced viral loads and enhanced mucosal barrier function.
Another study, published in 2024 by Brazilian researchers, examined the antiviral activity of berbamine dihydrochloride against Mayaro virus (MAYV). The in vitro results demonstrated that berbamine can interfere with viral replication, offering potential as a candidate for neglected tropical disease therapeutics.
Surprisingly, a structural analysis study using MicroED (Microcrystal Electron Diffraction) revealed that two commercial samples labeled as “berbamine dihydrochloride” were actually oxyacanthine dihydrochloride polymorphs. This finding emphasizes the critical need for accurate chemical validation in research-grade compounds.
Together, these studies reinforce that berbamine dihydrochloride is more than just a natural compound — it’s an emerging tool in biomedical innovation, with broad implications across virology, oncology, and drug quality assurance.
Therapeutic Applications and Benefits of Berbamine Dihydrochloride
Berbamine dihydrochloride is increasingly recognized for its broad-spectrum therapeutic potential, particularly in the fields of oncology, virology, and inflammation-related disorders. While most findings are currently preclinical, the results point toward a multifunctional bioactive molecule with compelling pharmacological benefits.
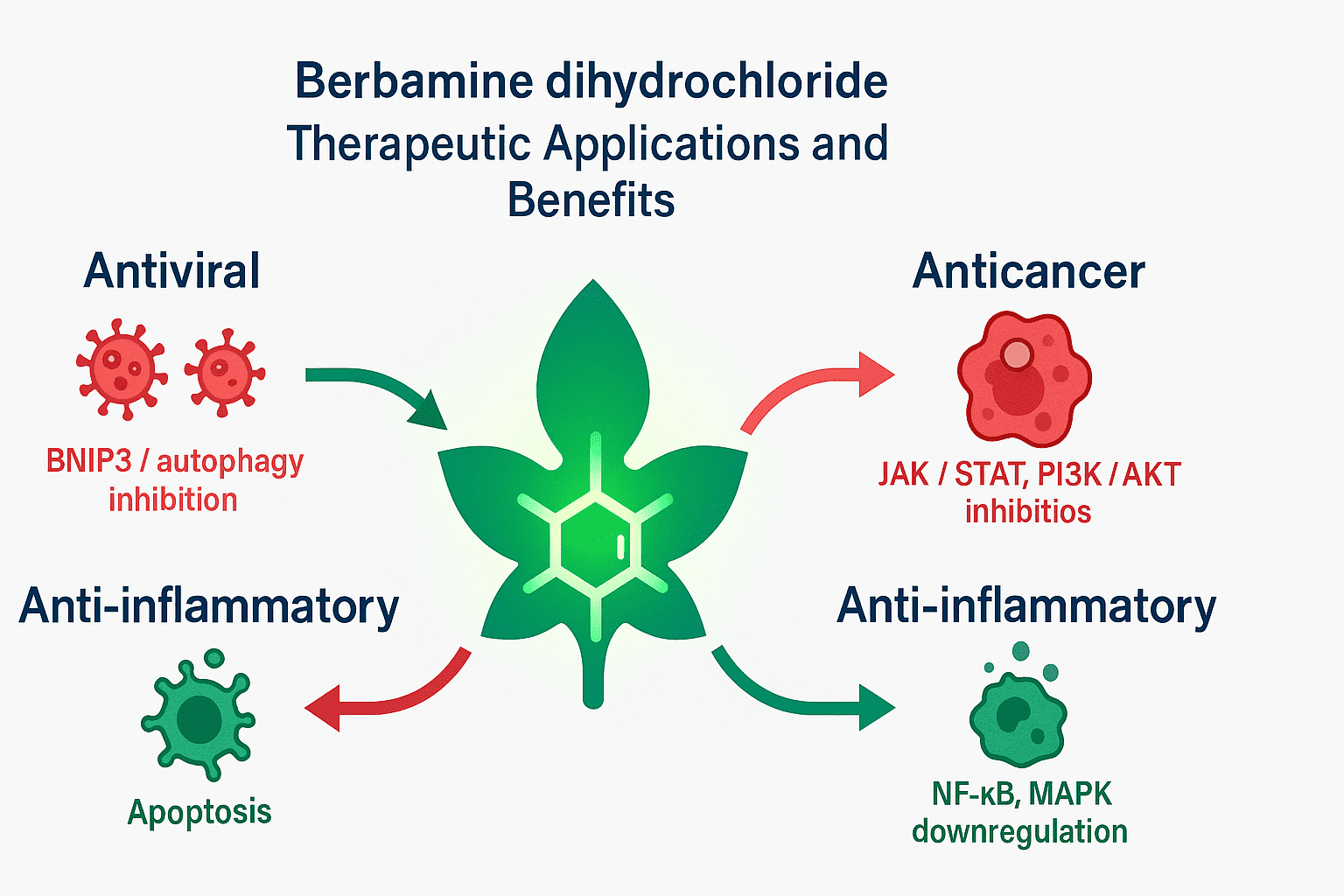
1. Antiviral Potential
One of the most promising areas of research is its antiviral activity. Berbamine dihydrochloride has demonstrated effectiveness against RNA viruses such as Mayaro virus and SARS-CoV-2. By modulating autophagy pathways — specifically inhibiting BNIP3-related viral exploitation of host cells — it reduces viral replication and supports mucosal barrier integrity. This opens possibilities for its inclusion in therapeutic strategies against emerging viruses.
2. Anticancer Effects
Berbamine has been shown to suppress tumor growth, especially in leukemia, liver, and breast cancers, by targeting key signaling pathways such as JAK/STAT, NF-κB, and PI3K/AKT. It not only inhibits proliferation but can also induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells, showing potential as an adjunct to chemotherapy.
3. Immunomodulatory and Anti-inflammatory Effects
Beyond antiviral and anticancer applications, berbamine exhibits anti-inflammatory properties by downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines. This could make it useful in treating autoimmune and chronic inflammatory conditions.
While clinical trials are still lacking, the compound’s multitargeted effects offer a strong case for its advancement in drug development. It may eventually become part of integrative therapeutic strategies for virus-related cancers, inflammatory syndromes, and emerging infectious diseases.
Availability, Safety, and Final Thoughts on Berbamine Dihydrochloride
Although berbamine dihydrochloride is gaining traction in scientific literature, it is currently not approved for clinical use and is available only for research purposes. Typically, it can be purchased through specialty chemical suppliers and laboratory reagent vendors that provide certified purity for in vitro or in vivo experimental use.
Because it’s a lab-grade compound, consumers and non-researchers are cautioned not to use berbamine dihydrochloride as a supplement or medication. Its pharmacokinetics, toxicity profile, and long-term effects in humans are not yet fully understood.
Safety and Quality Concerns
A notable 2025 study using MicroED (Microcrystal Electron Diffraction) revealed that some commercially available samples labeled as “berbamine dihydrochloride” were actually oxyacanthine dihydrochloride polymorphs, highlighting the potential for chemical mislabeling or cross-contamination. This underscores the importance of sourcing from reputable suppliers and conducting compound validation prior to use.
Toxicology data on berbamine itself suggest it can influence cell cycle progression, immune signaling, and mitochondrial function. While this makes it pharmacologically interesting, it also raises concerns for off-target effects or organ-specific toxicity if improperly used.
Final Thoughts
Berbamine dihydrochloride stands out as a natural compound with significant therapeutic promise, particularly for viral infections, cancer, and immune regulation. However, its role remains confined to the lab for now. Continued investment in preclinical and clinical trials will be crucial to unlocking its full potential and ensuring its safety and efficacy for human health applications.
References
Sanches, B. C. (2024). Estudo in vitro da ação do composto Berbamina como antiviral contra o MAYV. Universidade Estadual Paulista.
https://repositorio.unesp.br/entities/publication/d4fea12f-1418-4d5c-a577-aa1eae050db9
Rader, A. G., Cloherty, A. P. M., Patel, K. S., et al. (2025). Autophagy-enhancing strategies to promote intestinal viral resistance. Autophagy Reports, 2(1), 15–27.
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/27694127.2025.2514232